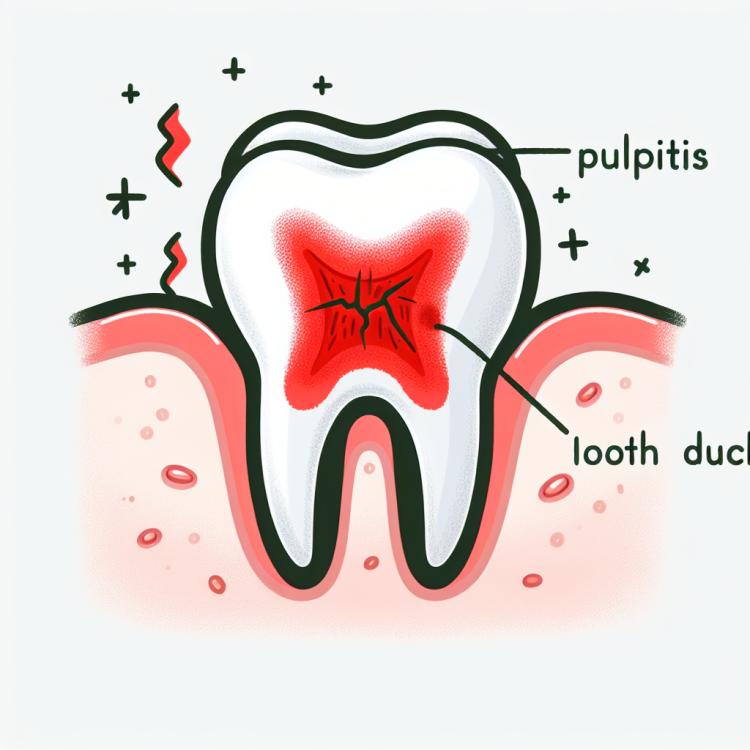
Pulpitis: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
- Understanding pulpitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Factors contributing to the development of pulpitis
- Main manifestations of pulpitis
- Expert opinion on the treatment of pulpitis
- Methods for diagnosing pulpitis
- Methods of treating pulpitis
- Prevention measures for pulpitis
- Amazing aspects of pulpitis
- FAQ
Understanding pulpitis: symptoms, causes, and treatment
Pulpitis is an inflammatory disease of the dental pulp caused by various factors, including caries, trauma, or infections. The main symptoms of pulpitis are acute toothache, sensitivity to cold and heat, swelling of the gums around the affected tooth. The diagnosis of pulpitis includes a clinical examination of the teeth, radiography, and sometimes, electric pulp testing.
The treatment of pulpitis directly depends on the degree of inflammation of the pulp. In the case of acute pulpitis, root canal treatment may be required to remove the inflamed tissue. Chronic pulpitis often requires tooth canal treatment. Effective methods for treating pulpitis include the use of antibiotics, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as professional oral hygiene.
Factors contributing to the development of pulpitis
The causes of pulpitis can be diverse and include dental caries, trauma, developmental anomalies of teeth, as well as the impact of chemical and physical irritants on the dental pulp. Caries is one of the main causes of pulpitis, as bacteria that penetrate the tooth due to damaged enamel trigger an inflammatory process in the pulp.
Dental injuries caused by impact, falls, or other effects can also lead to the development of pulpitis. Developmental anomalies of the teeth, such as improper formation of the roots or the presence of additional roots, can also increase the risk of inflammation of the dental pulp. It is important to promptly consult a dentist at the first signs of pulpitis to prevent complications and preserve dental health.
- Tooth decay: the destruction of tooth enamel by bacteria can lead to the development of pulpitis due to inflammation of the pulp.
- Tooth injuries: blows, falls, or other traumatic impacts can cause inflammatory processes in the pulp.
- Chemical irritants: the influence of aggressive chemicals on the dental pulp can contribute to the development of pulpitis.
- Physical irritants: overcooling or overheating of teeth, caused by consuming hot or cold drinks, can be a reason for pulp inflammation.
- Dental development anomalies: the presence of additional roots, improper tooth formation, or other anomalies can increase the risk of pulpitis development.
Main manifestations of pulpitis
The symptoms of pulpitis can vary depending on the degree of the inflammatory process and the individual characteristics of the patient. The main manifestations of pulpitis usually include painful sensations, sensitivity to cold or heat, increased pain when biting, and swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of the affected tooth. Patients may also note increased pain when consuming sweet or sour foods, which is related to irritation of the damaged pulp.
In some cases, it is possible to experience a worsening of pain at night, which can interfere with normal sleep. In chronic pulpitis, the symptoms may be less pronounced; however, the sensitivity of the tooth to various irritants still persists. Early detection of pulpitis symptoms and timely consultation with a dentist will help prevent serious complications and maintain dental health.
- Pain and sensitivity: One of the main symptoms of pulpitis is pain in the affected tooth, which can intensify when in contact with irritants such as hot or cold food.
- Swelling and redness: Inflammation of the pulp can cause swelling of the mucous membrane around the tooth, as well as its redness due to increased blood flow.
- Increased pain when biting: Patients often note an increase in pain when pressure is applied to the affected tooth, for example, when biting hard food.
- Sensitivity to sweet and sour: A tooth with pulpitis may react to sweets and acids, causing discomfort and increased pain.
- Worsening at night: Some patients may experience increased pain at night, which can interfere with normal sleep and require urgent dental attention.
Expert opinion on the treatment of pulpitis
Experts’ opinions in the field of dentistry regarding the treatment of pulpitis emphasize the importance of early medical assistance to prevent complications. The unique characteristics of each case of pulpitis may require a personalized approach to treatment, making consultation with a qualified dentist a necessary part of effective therapy. Experts also highlight the importance of conducting a comprehensive examination, including radiographic diagnostics, to determine the extent of dental pulp damage and to select the optimal treatment method.
Modern methods of treating pulpitis can vary from conservative procedures, such as the removal of affected tissue and canal treatment, to surgical interventions in cases of severely advanced disease. Experts recommend combining medication treatment with professional cleaning and preventive measures to avoid recurrences of pulpitis and to maintain the patient’s teeth in the long term.

Methods for diagnosing pulpitis
Diagnosis of pulpitis involves conducting a thorough clinical examination of the patient and assessing symptoms such as pain when biting, increased sensitivity of the tooth to various stimuli, and swelling of the mucous membrane. An important part of the diagnosis is tactile examination of the tooth using instruments, which can allow the dentist to assess the sensitivity of the pulp and the presence of signs of inflammation.
To clarify the diagnosis and determine the extent of damage to the dental pulp, radiographic methods such as X-rays or CT scans may be used. These methods allow for the evaluation of the condition of the root canals, the presence of cysts, changes in the structure of the bone tissue, and help the dentist decide on the necessity of treating pulpitis. It is important to conduct a complete diagnosis to determine an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan for the patient with pulpitis.
- Clinical examination: the doctor assesses symptoms such as pain, tooth sensitivity, and changes in the mucous membrane.
- Tactile examination: conducted to assess the condition of the dental pulp, determine its sensitivity, and signs of inflammation.
- X-ray: this method involves taking X-ray images or CT scans to examine the root canals, the condition of the bone tissue, and identify possible pathologies.
- Electronic tomography: allows obtaining a three-dimensional image of the tooth structure and its roots for a more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Pulp tests: include special tests, such as cold or heat tests, which help determine the condition of the dental pulp and its reactivity.
Methods of treating pulpitis
In cases of acute severe inflammation, pain relief, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory medications may be required. If the tooth is contraindicated for treatment, extraction may be necessary. After undergoing endodontic treatment, follow-up with a dentist is recommended to check the effectiveness of the procedure and prevent possible complications.
- Endodontic treatment: the procedure of removing pulp, cleaning, and filling the tooth canal to eliminate inflammation and preserve the tooth.
- Anesthesia: the use of analgesics and pain-relieving medications to reduce pain and discomfort for the patient during treatment.
- Use of antibiotics: if necessary, the use of antibiotics to combat infection and prevent its spread.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: the use of medications to reduce inflammation and improve the overall condition of the tooth and surrounding tissues.
- Monitoring and control: regular visits to the dentist after treatment to assess results, prevent complications, and maintain tooth health.
Prevention measures for pulpitis
Avoiding habits that can lead to tooth damage, such as smoking, consuming acidic drinks, and excessive intake of sugary foods, is also important for preventing pulpitis. Proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and minerals, helps strengthen tooth enamel and reduces the risk of cavities, which also lowers the likelihood of developing pulpitis.
- Regular oral hygiene: daily tooth brushing, use of dental floss, and mouthwashes help prevent bacterial buildup and the development of cavities.
- Regular visits to the dentist: preventive examinations and teeth cleaning help identify problems at an early stage and prevent the development of pulpitis.
- Avoiding harmful habits: quitting smoking, limiting the consumption of acidic drinks and sweet foods reduces the risk of developing oral diseases, including pulpitis.
- Proper nutrition: consuming nutritious foods rich in vitamins and minerals helps strengthen tooth enamel and maintain dental health.
- Using protective gear: wearing protective equipment during sports or work prevents injuries that can lead to pulpitis.
Amazing aspects of pulpitis
Another interesting fact is that pulpitis can manifest in different forms, from acute, accompanied by intense pain, to chronic, with less pronounced symptoms. Scientists and doctors are constantly working to improve the methods of diagnosis and treatment of pulpitis to provide patients with more effective and comfortable care for this condition.