Heel spur: diagnosis, causes, and treatment methods
Heel spur: key aspects
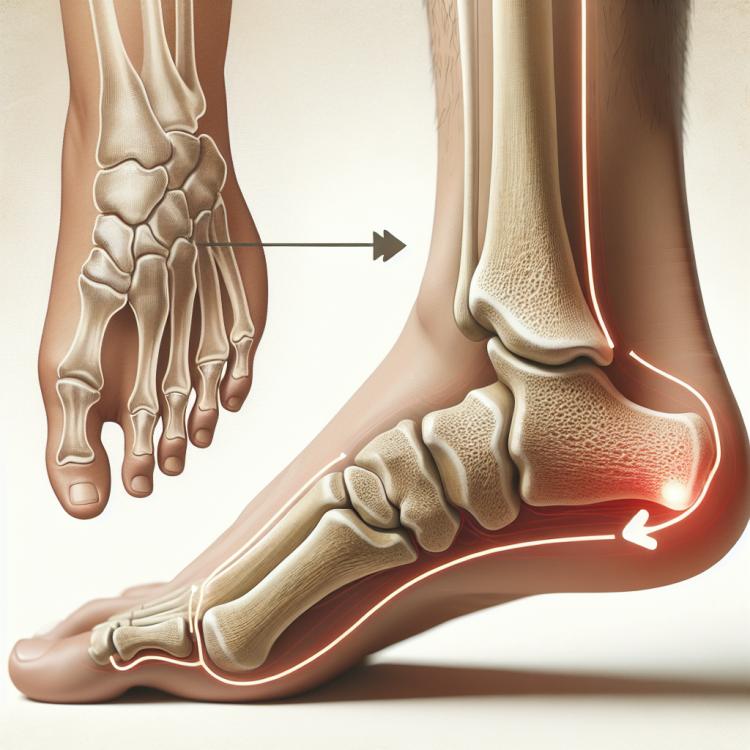
The heel spur is a pathological formation in the area of the heel bone, occurring as a result of chronic inflammation of the heel ligament. The main symptom is sharp pain in the heel, which intensifies with load on the foot and when rising on the toes. The causes of heel spur development can include mechanical injuries, overloading of the foot, as well as prolonged standing.
For the diagnosis of heel spur, X-ray of the heel bone and ultrasound of the foot are conducted. Treatment measures include the use of orthopedic shoes, wearing special insoles, physiotherapy, massage, stretching of the foot muscles, exercises to strengthen the calf and foot muscles. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Causes of heel spur formation
The causes of heel spurs include repetitive strain on the ligaments and muscles of the foot, leading to microtraumas of the heel bone. This can occur due to excessive strain from sports activities, wearing uncomfortable shoes, or due to biomechanical disorders of the foot. Additionally, risk factors may include obesity, foot compression from prolonged walking or standing, and age-related changes in foot structure.
- Overstrain of ligaments and muscles of the foot: repeated micro-injuries to the heel bone due to recurring loads.
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes: shoes with poor cushioning or support can contribute to the development of heel spurs.
- Biomechanical disorders of the foot: anomalies in the structure of the foot can create additional pressure on the heel bone.
- Risk factors, including obesity: excess weight increases the load on the foot and may contribute to the development of pathology.
- Prolonged walking or standing: compression of the foot due to prolonged loads can be one of the causes of heel spurs.
Symptoms of heel spur
Symptoms of a heel spur may include pain in the heel area, especially with the first steps after sleeping or prolonged rest. The appearance of discomfort when pressure is applied to the heel or during active movement is also characteristic. Patients may also experience inflammation and swelling in the heel area, which may be accompanied by redness of the skin.
In addition, patients with heel spurs may experience burning and numbness in the heel area, as well as a sensation of a “spur” in the heel region during sports activities or prolonged periods of walking. Symptoms may intensify when wearing shoes with a tight back or in the presence of flat feet, which increases the load on the foot.
- Heel pain: patients may experience pain with the first steps after sleeping or prolonged rest.
- Inflammation and swelling: observed in the heel area, often accompanied by skin redness.
- Burning and numbness: patients may experience these unpleasant sensations in the heel area.
- Feeling of “spur”: patients may feel the presence of a “spur” in the heel area, especially during physical activity.
- Worsening of symptoms: symptoms of heel spur may worsen when wearing uncomfortable shoes or in the presence of flat feet, causing additional discomfort.
Expert opinions on treating heel spurs
Experts in the field of medicine agree that the treatment of heel spurs should be comprehensive and include several approaches. The main focus is on reducing inflammation and pain in the heel area. Physical therapy, including exercises to strengthen the foot muscles and stretch the Achilles tendon, can help improve symptoms.
Experts also recommend the use of orthopedic shoes or insoles, which can reduce the load on the heel and improve foot support. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. Additional treatment methods may include ultrasound therapy, laser treatment, or shockwave therapy.

Diagnosis of heel spur
The diagnosis of heel spurs begins with a medical examination, during which the doctor assesses the symptoms and the patient’s medical history. X-ray imaging of the heel is often used to confirm the diagnosis, allowing visualization of the spur and evaluation of its size. Additional tests, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, may sometimes be conducted to study the condition of the tissues and structures of the foot in more detail.
It is important to remember that the diagnosis of heel spurs requires a comprehensive approach and consideration of all possible factors influencing their occurrence. After conducting all necessary examinations, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment aimed at reducing pain and improving the patient’s foot condition.
- Medical examination: the doctor assesses the symptoms and medical history of the patient.
- X-ray of the heel: allows you to see the presence of a spur and evaluate its size.
- Ultrasound examination: an additional diagnostic method for a more detailed study of the condition of the foot tissues.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: allows for more accurate images of the structures of the foot to clarify the diagnosis.
- Comprehensive approach: necessary to consider all factors affecting the occurrence of heel spur.
Treatment of heel spur
In cases where conservative methods do not provide adequate relief, a doctor may recommend steroid or anti-inflammatory injections to reduce inflammation in the heel area. In some cases, if the heel spur becomes chronic and interferes with normal daily activities, surgical intervention may be necessary, such as removing the spur or correcting foot deformity.
- Use of orthopedic shoes: specially selected shoes help distribute the load on the foot evenly, reducing pressure on the heel.
- Physical therapy and exercises: regular stretches and exercises strengthen the muscles of the foot and calf, improving joint mobility and reducing pain sensations.
- Steroid injections: injections directly into the heel area can help relieve inflammation and reduce pain sensations.
- Use of orthoses and insoles: special orthoses and insoles help reduce the load on the heel and provide proper support for the foot.
- Surgical treatment: in extreme cases, when other methods are ineffective, surgical intervention may be required to remove a heel spur or correct foot deformities.
Prevention of heel spur
To prevent heel spurs, it is also recommended to maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight increases strain on the foot. Maintaining an active lifestyle, with regular sports activities that include exercises to strengthen the foot muscles, also helps reduce the risk of developing heel spurs.
- Wearing comfortable shoes: Choosing the right shoes with good cushioning and support will help reduce the load on the foot and prevent injuries.
- Regular stretching of foot and calf muscles: Stretching exercises for the muscles will help reduce strain and prevent potential injuries.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight increases the load on the foot and can contribute to the development of heel spurs.
- Active lifestyle: Regular physical activity, including exercises to strengthen foot muscles, will help reduce the risk of developing heel spurs.
- Monitoring foot position: Maintaining the correct foot position and avoiding improper loads will help prevent the development of pathologies.
Interesting facts about heel spur
Another interesting fact is that heel spurs can develop not only in adults but also in teenagers, including athletes and active adolescents. Given that teenagers’ bone tissue is not fully developed yet, the influence of intense physical activities on the heel during growth and development may be a factor.