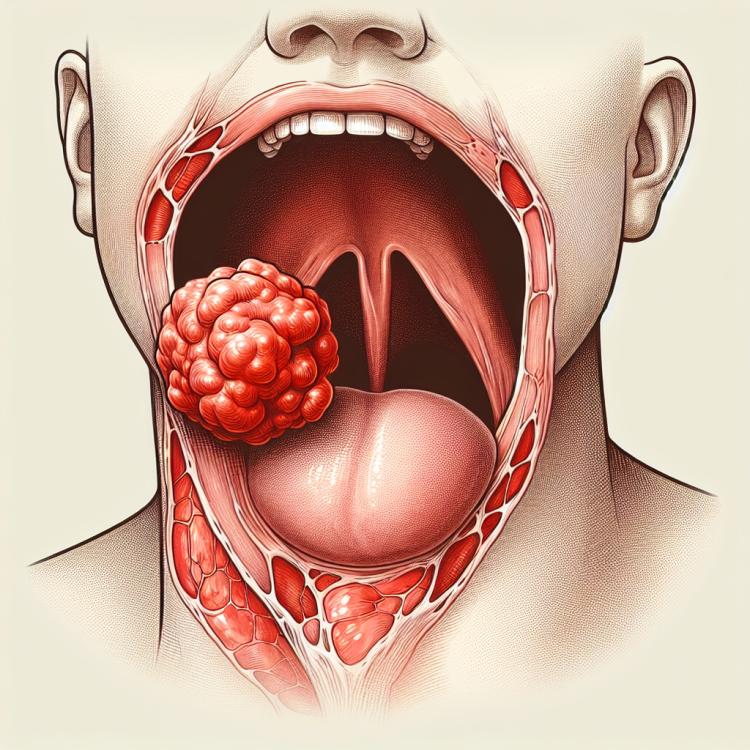
Throat cancer: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
- Definition of throat cancer
- Risk factors for the development of throat cancer
- Clinical manifestations of throat cancer
- Approaches to the treatment of throat cancer: an expert’s perspective
- Methods of diagnosing pharyngeal cancer
- Treatment options for throat cancer
- Measures to prevent throat cancer
- Unusual facts about throat cancer
- FAQ
Definition of throat cancer
Pharyngeal cancer, an oncological disease, is characterized by the malignant formation in the tissues of the larynx. The pharynx is an anatomical structure that connects the mouth and the esophagus, where tumors develop under the influence of various factors such as tobacco smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, the human papillomavirus (HPV), and genetic predisposition. Pharyngeal cancer often manifests with various symptoms, including changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, throat pain, cough, as well as loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss.
Risk factors for the development of throat cancer
Risk factors for the development of throat cancer include various aspects of life and the environment. One of the main factors is tobacco use, including smoking and the use of tobacco products. Nicotine and other substances found in tobacco can harm the throat and promote oncological processes.
Another important risk factor is frequent alcohol consumption. Alcohol contributes to damage to the mucous membrane of the throat and can increase the likelihood of cancerous cells developing. The combination of smoking and alcohol consumption further increases the risk of developing throat cancer.
- Tobacco use: Smoking and the use of tobacco products are major risk factors for the development of throat cancer due to the harmful substances contained in tobacco.
- Alcohol consumption: Frequent alcohol consumption can damage the mucous membrane of the throat and increase the likelihood of developing cancerous cells.
- Viruses and infections: Some viruses, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV), can increase the risk of throat cancer.
- Prolonged exposure to aggressive environmental factors: Continuous exposure to aggressive chemicals or industrial waste can increase the risk of developing oncological diseases.
- Genetic predisposition: Hereditary factors and genetic mutations can also play a role in the occurrence of throat cancer.
Clinical manifestations of throat cancer
The clinical manifestations of throat cancer may include symptoms such as persistent or worsening difficulty swallowing, the appearance of pain or discomfort in the throat, changes in voice or hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, as well as the appearance of lumps in the neck. Patients may also experience a feeling of pressure in the throat or difficulty passing food through the esophagus.
It is important to note that the symptoms of throat cancer can vary depending on the location of the tumor in the throat. Patients with tumors in different parts of the throat may exhibit different disease manifestations. Early consultation with a doctor at the first signs of changes in the throat, especially with the presence of risk factors, can aid in the early detection of throat cancer and the initiation of effective treatment.
- Difficulty swallowing: persistent or worsening difficulty in passing food through the throat may be one of the first signs of throat cancer.
- Sore throat or discomfort: the appearance of pain or discomfort in the throat, especially when swallowing, may be a warning signal of disease.
- Changes in voice or hoarseness: the onset of hoarseness, especially if the symptom persists for an extended period, may be associated with laryngeal or pharyngeal cancer.
- Unexplained weight loss: unexplained weight loss, particularly in the absence of changes in diet or physical activity, may be a sign of a pathological process.
- Enlargement of cervical lymph nodes: the appearance of nodes in the neck, especially with an increase in their size, may indicate the spread of cancer cells from the pharynx to surrounding tissues and lymph nodes.
Approaches to the treatment of throat cancer: an expert’s perspective
Experts in the field of oncology agree that the treatment of throat cancer requires a comprehensive approach, including surgical intervention, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or their combination depending on the stage of the disease. Surgical removal of the tumor is often recommended in cases where throat cancer is at an early stage of development and has not spread beyond the throat.
In advanced stages of throat cancer, an effective treatment method is combined therapy, which includes chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The use of modern methods of radiation therapy and chemotherapy allows for good outcomes in the treatment of throat cancer, improving the prognosis and quality of life for patients.

Methods of diagnosing pharyngeal cancer
Diagnosis of throat cancer includes several methods that allow for the determination of the presence of a tumor, its stage, and characteristics. One of the primary methods is fiber laryngoscopy, in which the doctor visually examines the larynx and pharynx using a flexible tube with a light source and a camera at the end. Computed tomography (CT) may be used for a more detailed study of the laryngeal and neck area, determining tumor size and the presence of metastases.
Additional diagnostic methods include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), biopsy to obtain a tissue sample for pathological analysis and determine the type of cancer, as well as additional laboratory tests to detect cancer cell markers. Effective diagnosis plays an important role in determining treatment tactics and prognosis for patients with throat cancer.
- Fibrolaryngoscopy: Visual examination of the larynx and pharynx using a flexible tube with a camera.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Using X-rays to create detailed images of the larynx and neck area.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Using magnetic fields to create images of internal structures.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): A method of imaging based on detecting radioactive markers in the patient.
- Biopsy: Taking a tissue sample for pathological analysis and determining the type of cancer.
Treatment options for throat cancer
In cases of advanced stages of throat cancer, combined treatment may be required, involving several methods either simultaneously or sequentially. Effective treatment of throat cancer usually requires a comprehensive approach involving oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and other specialists to achieve the best outcome and increase the chances of patient recovery.
- Surgical treatment: Involves the removal of the tumor and often adjacent tissues for thorough clearance. It can be used as the primary method of treatment or in combination with other therapies.
- Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells. It may be prescribed before or after surgery or as a sole treatment method.
- Chemotherapy: Involves the use of drugs that kill cancer cells, often in combination with other methods. It is used to treat throat cancer at various stages of the disease.
- Targeted therapy: Aims at specific molecular targets in cancer cells and may be prescribed in combination with other treatment methods to improve outcomes.
- Immunotherapy: Involves stimulating the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. It may be used in some patients with throat cancer to enhance treatment effectiveness.
Measures to prevent throat cancer
Regular medical check-ups and screening programs play an important role in the early detection and diagnosis of throat cancer, which can enhance treatment effectiveness and improve prognosis for patients. Educating the public about risk factors and preventive measures is also crucial for raising awareness about the disease and aiding in its prevention.
-
– Quitting smoking and the use of tobacco products. Nicotine and other substances found in tobacco increase the risk of developing throat cancer and other diseases.
– Limiting alcohol consumption. Alcohol consumption increases the likelihood of developing throat cancer, so moderate consumption of alcoholic beverages may reduce the risk of disease.
– Adhering to regular medical check-ups. Early detection of changes in the larynx and pharynx allows for treatment to begin at the early stages of the disease.
– Nutrition rich in nutrients. A healthy and balanced diet contributes to overall health and may reduce the risk of developing throat cancer.
– Education on risk factors and primary prevention. Increased awareness of lifestyle and risk factors can help individuals make more informed decisions to prevent throat cancer.
Unusual facts about throat cancer
Additionally, unique genetic mutations may also play a role in the occurrence of throat cancer in some individuals. These genetic changes can affect the body’s ability to fight cancer cells and increase the likelihood of the disease. Understanding these unusual factors may aid in developing more effective prevention and treatment strategies for throat cancer.