Rectovaginal fistula: diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis
- Definition of rectovaginal fistula
- Etiology of rectovaginal fistula
- Manifestations of rectovaginal fistula
- Views of specialists on the treatment methods for rectovaginal fistula
- Methods for diagnosing rectovaginal fistula
- Therapy for rectovaginal fistula
- Measures to prevent rectovaginal fistula
- Facts about rectovaginal fistula
- FAQ
Definition of rectovaginal fistula
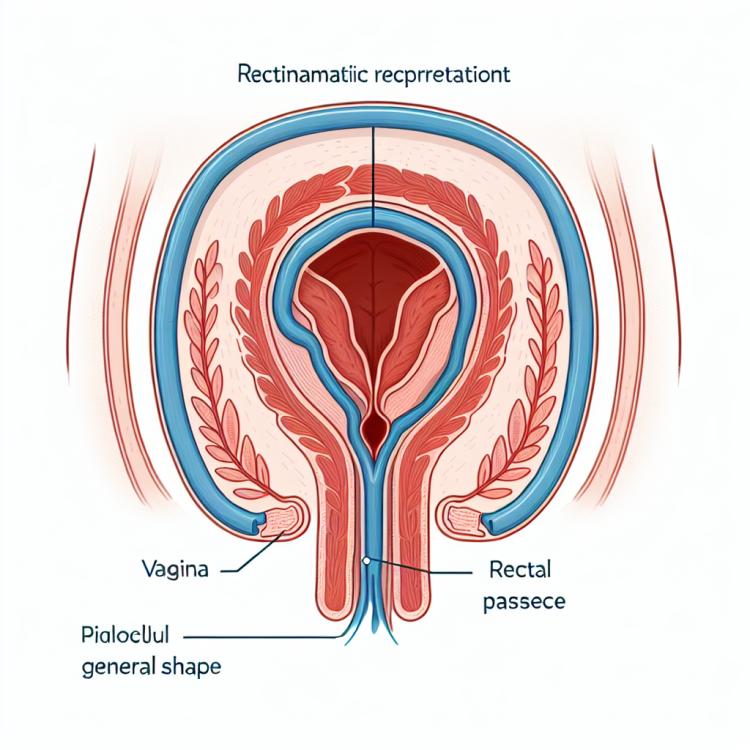
A rectovaginal fistula is a pathological condition characterized by an abnormal opening between the rectum and the vagina. This type of fistula is an open channel between these two cavities, leading to unwanted exchange of contents such as intestinal gases or feces. Rectovaginal fistulas typically result from surgical operations, trauma, or infections, and can cause significant discomfort and complications for the patient.
Proper diagnosis and treatment of a rectovaginal fistula require a comprehensive approach and an individualized treatment plan, which may include conservative methods such as medication therapy, as well as surgical interventions depending on the characteristics and severity of the fistula. It is important to seek timely assistance from qualified specialists for accurate diagnosis and to determine the optimal treatment for this pathological condition.
Etiology of rectovaginal fistula
Rectovaginal fistula is a pathological condition characterized by an abnormal opening between the rectum and the vagina. Its causes can be diverse. Possible factors contributing to the development of a rectovaginal fistula include trauma during childbirth, surgical interventions in the pelvic area, infections, inflammatory processes, and malignant tumors that cause tissue destruction and the formation of a fistulous tract between the rectum and the vagina.
- Injuries during childbirth: prolonged and difficult labor can damage the tissues between the rectum and the vagina.
- Surgical interventions in the pelvic area: surgical operations in the pelvic region can lead to tissue damage and the formation of a fistula.
- Infections: infections such as abscesses or sexually transmitted diseases can cause the development of a rectovaginal fistula.
- Inflammatory processes: chronic inflammation in the pelvic organs can lead to the formation of a fistula between the rectum and the vagina.
- Malignant tumors: malignant tumors in the pelvic area can cause tissue destruction and the occurrence of a rectovaginal fistula.
Manifestations of rectovaginal fistula
The symptoms of a rectovaginal fistula can vary depending on its size, location, causes, and the presence of complications. Typically, patients complain of discomfort in the pelvic area and rectum, as well as purulent-mucous discharge from the vagina. The most common symptoms include pain in the area of the rectum and vagina, especially during bowel movements or sexual intercourse, as well as the presence of an unpleasant odor or vaginal itching.
In addition, patients with a rectovaginal fistula often experience frequent urogenital infections, including vaginal dysbiosis and urinary infections. It is important to pay attention to these signs and promptly consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Pain in the pelvic area and rectum: pain may occur during defecation or sexual intercourse, and may also be constantly noticeable.
- Presence of purulent-mucous discharge: fluid may be constantly or periodically discharged from the vagina and have an unpleasant odor.
- Urogenital infections: frequent exacerbations of vaginal dysbiosis and urinary infections may indicate the presence of a rectovaginal fistula.
- Unpleasant odor: observed due to the leakage of rectal contents into the vagina and its effect on the microbiota.
- Vaginal itching: occurs due to changes in the vagina caused by contact of intestinal secretions with its mucous membrane.
Views of specialists on the treatment methods for rectovaginal fistula
Experts in the field of medicine note that the choice of treatment method for rectovaginal fistula depends on many factors, including the size and location of the fistula, the presence of complications, the overall condition of the patient, and their medical history. Traditional treatment methods may include surgical intervention, the use of medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, or combined methods.
Modern technologies and techniques allow for effective treatment of rectovaginal fistulas, minimizing the risk of complications and improving the prognosis for patients. Moreover, an important aspect is the individualized approach to each case, taking into account the patient’s characteristics and the optimal combination of treatment methods to achieve the best results.

Methods for diagnosing rectovaginal fistula
Various methods are used for diagnosing a rectovaginal fistula, including visual examination, digital examination of the vagina and rectum, as well as instrumental studies such as rectoscopy, colonoscopy, and cystoscopy. An important method is gastroscopy, which allows for the visualization of pathological changes in the mucous membranes of the rectum and vagina.
Additionally, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be required for an accurate diagnosis of the rectovaginal fistula. These methods help determine the exact location and size of the fistula, which is crucial for determining the optimal treatment method. All diagnostic procedures are performed by specialists and aim to establish an accurate diagnosis and plan further treatment for the patient.
- Visual inspection: The doctor conducts an external examination of the genital organs and urinary tract to identify characteristic signs of a fistula.
- Digital examination: Through a digital exam, the doctor assesses the condition of the vaginal and rectal tissues for any pathological changes.
- Instrumental studies: It is recommended to perform rectoscopy, colonoscopy, and cystoscopy to confirm the diagnosis and determine the characteristics of the fistula.
- Gastroscopy: This method helps the doctor to examine and evaluate the mucous membrane of the rectum and vagina to identify changes related to rectovaginal fistula.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): These methods are essential for accurate visualization of the fistula, determining its size and location.
Therapy for rectovaginal fistula
- Conservative therapy: Includes the use of medications, dietary regulation, and hygienic procedures to improve tissue healing and prevent infections.
- Medication treatment: Involves the use of antibiotics to combat infection, as well as other drugs aimed at healing and strengthening tissues.
- Surgical interventions: May include operations to remove fistulas, plastic surgeries to restore damaged tissues, as well as the use of reconstruction techniques to restore normal anatomy.
- Physiotherapy: May be prescribed to improve blood flow, stimulate wound healing, and strengthen pelvic floor muscles.
- Rehabilitation activities: Include restorative treatment programs, physical rehabilitation, psychological support, and recommendations for preventing disease recurrence.
Measures to prevent rectovaginal fistula
As part of preventive measures, timely consultation with a doctor at the first signs of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs can be recommended, careful hygiene practices, and avoiding uncontrolled use of medications that can disrupt the microflora and lead to infections. Adhering to hygiene rules, regular visits to the doctor for preventive examinations, and timely treatment of other pathologies can help reduce the likelihood of developing a rectovaginal fistula.
- Avoid injuries and strains in the pelvic area and rectum: prevent injuries when engaging in sports or intense physical exercises.
- Follow hygiene rules: regular washing of intimate areas and careful conduct of hygiene procedures can help prevent the development of infections.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: regular physical activity and proper nutrition contribute to the health of the body and normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Consult a doctor at the first signs of inflammatory diseases: adhering to preventive examinations and timely treatment of other pathologies helps reduce the likelihood of developing a rectovaginal fistula.
- Avoid uncontrolled medication intake: experiencing the effects of medications without a doctor’s recommendations can disrupt the microflora and contribute to the development of infections.
Facts about rectovaginal fistula
Another interesting fact is that the prevention of rectovaginal fistula includes regular visits to a doctor, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following hygiene rules. Conducting preventive measures and timely treatment of other diseases can help reduce the risk of developing this pathological condition.