Rosacea: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
Introduction to rosacea: possible causes and symptoms
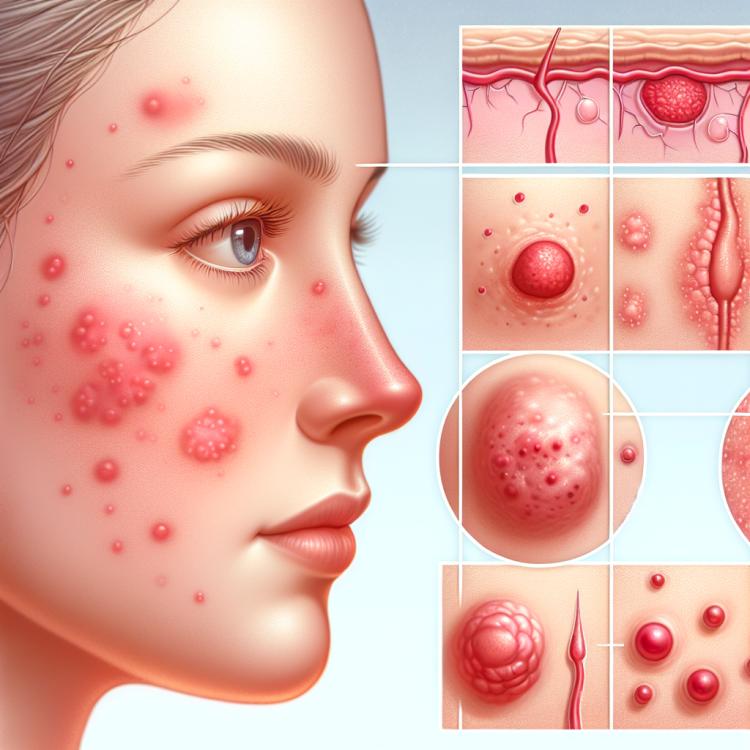
Rosacea, also known as couperose, is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by vasodilation and papulopustules. Its development is based on various factors, including genetic predisposition, impaired regulation of vascular tone, inflammation, and an imbalance of skin microbiota.
Moreover, patients with rosacea may experience increased skin sensitivity, which exacerbates reactions to external irritants. Symptoms of the disease may include redness, papules, pustules, telangiectasia, and hyperplasia of sebaceous glands. It is important to identify possible causes of rosacea development for effective treatment and management of the symptoms of this condition.
Factors contributing to the development of rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by frequent flare-ups and remissions. While the exact causes of rosacea remain unclear, there are several factors that may contribute to its onset. Uncontrolled dilation of blood vessels, increased skin sensitivity, genetic predisposition, exposure to ultraviolet rays, and an imbalance of microorganisms on the skin may play a role in the development of this condition.
- Capillary expansion: The widening of blood vessels in the facial skin can increase redness and inflammation in rosacea.
- Genetic predisposition: Hereditary factors may play a role in the development of rosacea, as evidenced by the presence of the condition among family members.
- Sensitive skin: People with increased skin sensitivity may have a higher risk of developing rosacea.
- Exposure to external factors: Exposure to ultraviolet rays, wind, cold, and strong odors can contribute to flare-ups of rosacea.
- Microorganism imbalance: Changes in the skin’s microbiome can create a conducive environment for the development of inflammation and symptoms of rosacea.
How does rosacea manifest?
Rosacea manifests itself with a variety of symptoms, which often include red patches on the skin, increased sensitivity, inflammation, and rashes. These signs can be temporary or persistent, with periods of flare-ups and remissions. Patients with rosacea often experience increased redness in the central area of the face, such as the cheeks, forehead, nose, and chin, making it one of the characteristic manifestations of the condition. In some cases, patients with rosacea may also experience eye irritation, a prominent burning sensation, and a feeling of sand in the eyes, which is associated with a condition known as ocular rosacea.
- Red spots on the skin: rosacea often manifests as red, inflamed patches on the face, especially in the central area of the face.
- Increased sensitivity: patients with rosacea often experience increased sensitivity to cosmetic products, sunlight, and temperature changes.
- Inflammation and irritation of the skin: the skin of a patient with rosacea may be inflamed, irritated, and tender to the touch.
- Rashes and blisters: some people with rosacea may develop rashes or blisters on the skin, especially during flare-ups of the condition.
- Ocular rosacea: some patients with rosacea also experience eye irritation, a burning sensation, and discomfort, which may indicate ocular rosacea – a condition affecting the eyes.
Expert opinion on methods for treating rosacea
Dermatology experts consider a wide range of methods for treating rosacea, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. One of the main strategies is a comprehensive approach that includes medication, cosmetic procedures, and lifestyle regulation. Medical products, such as topical agents with metronidazole, azelaic acid, systemic antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs, may be used to reduce inflammation and improve skin condition in patients with rosacea.
Experts also emphasize the importance of protecting the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays, as sun exposure can exacerbate rosacea symptoms. Additionally, procedures such as laser therapy, electrosurgery, and photodynamic therapy may offer effective methods for improving the appearance of the skin and reducing the development of the vascular network characteristic of rosacea.

Methods for diagnosing rosacea
Diagnosis of rosacea is usually based on a clinical examination of the patient’s skin by a dermatologist. The doctor pays attention to typical symptoms such as red spots, inflammation, redness of the central area of the face, signs of meteorism, and the presence of rashes. To clarify the diagnosis and exclude other skin conditions, various additional methods may be used, including dermoscopy and skin biopsy, which allows confirming the presence of rosacea and excluding other pathologies with similar symptoms.
- Clinical examination: The specialist conducts a careful examination of the patient’s skin to identify typical symptoms of rosacea, such as red spots, inflammation, pink redness of the central area of the face, and rashes.
- Dermatoscopy: A method that allows the specialist to study skin samples under magnification, helping to identify features of skin structure and signs of rosacea.
- Skin biopsy: Taking a tissue sample for subsequent microscopic examination, which allows differentiation of rosacea from other skin diseases.
- Skin condition investigation: Various methods, such as electrocardiography or thermography, can be used to assess inflammatory changes and blood flow in the affected skin area.
- Blood tests: Some blood tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions that may mimic the symptoms of rosacea or contribute to the development of the disease.
Methods of treating rosacea
- Anti-inflammatory creams and gels: Some medications can help reduce inflammation and redness of the skin, which are key symptoms of rosacea.
- Systemic medications: In some cases, when rosacea manifests in a severe form, a doctor may prescribe systemic medications, such as antibiotics or retinoids, to control inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy methods, such as electrotherapy or ultrasound therapy, can help improve skin condition and reduce rosacea symptoms.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatment can be an effective method for narrowing dilated blood vessels and reducing skin redness in patients with rosacea.
- Surgical interventions: In some cases, surgical procedures, such as cryodestruction or electrocautery, may be recommended to improve the appearance of the skin in rosacea.
Prevention of rosacea
- Protection from solar radiation: Using sunscreen and wearing headwear helps protect the skin from ultraviolet rays, reducing the likelihood of rosacea flare-ups.
- Avoiding irritants: Avoiding spicy food, alcohol, stress, and extreme temperatures may help prevent disease exacerbation.
- Moisturizing and protecting the skin: Regularly moisturizing the skin, using gentle care products, and protecting the skin from adverse factors contribute to maintaining skin health.
- Healthy lifestyle: Adhering to a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, avoiding harmful habits, and moderate physical activity, may reduce the risk of developing rosacea.
- Regular consultations with a doctor: Visiting a dermatologist for preventive examinations and consultations will help timely identify the first signs of rosacea and prevent disease progression.