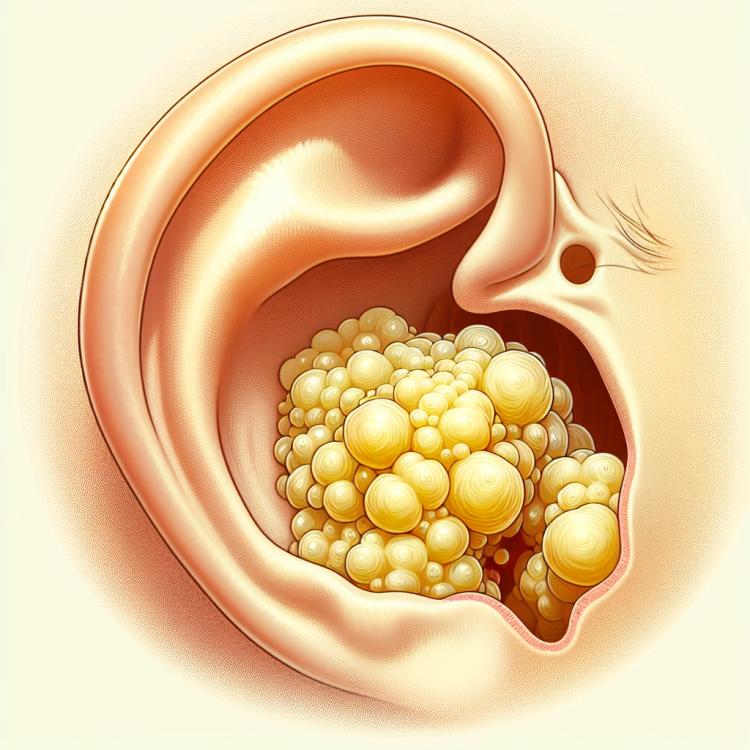
Sulfur plug: what is it and how to treat it
- Description of sulfur plug: symptoms, causes, and treatment methods
- Factors causing the formation of sulfur plug
- Possible symptoms of a sulfur plug
- Approaches to the treatment of sulfur plugs: expert opinions
- Methods for diagnosing a sulfur plug
- Methods for treating a sulfur plug
- Measures for the prevention of sulfur plug
- Amazing facts about sulfur plugs
- FAQ
Description of sulfur plug: symptoms, causes, and treatment methods
Ear wax blockage, or earwax impaction, is a blockage in the ear canal due to the accumulation of earwax formed by wax secretions. Symptoms may include hearing loss, tinnitus, pain, itching, or a sensation of pressure in the ear. Manifestations may intensify when chewing and swallowing.
Causes of earwax impaction may include excessive wax production, improper removal of wax, or the use of hearing aids. Treatment usually involves gentle irrigation of the ear canal with solutions that help soften the earwax, as well as the use of special ear drops.
Factors causing the formation of sulfur plug
The causes of earwax buildup can be numerous and depend on individual patient factors. One of the main factors contributing to the formation of earwax buildup is the excess earwax produced by the sebaceous glands in the ear canal. This can occur as a result of improper ear care, using chemically aggressive substances for cleaning earwax, as well as dysfunctions in the sebaceous glands due to pathologies or diseases of the auditory organs.
Other causes of earwax buildup can include a narrow or curved ear canal, anatomical features of the ear structure, as well as improper use of ear-inserting objects, which contributes to the compaction and accumulation of earwax. It is important to keep in mind that uncontrolled self-removal of earwax buildup can lead to its further compaction and packing, exacerbating the problem and complicating the treatment process.
- Excess earwax from sebaceous glands: improper ear cleaning can lead to excessive accumulation of earwax, promoting the formation of a wax plug.
- Improper ear hygiene: excessive use of chemically aggressive products or attempts to clean the ears with unsuitable objects can stimulate the formation of a wax plug.
- Anatomical features of the ear canal: a narrow or curved ear canal may contribute to wax accumulation and the formation of a plug.
- Disorders of sebaceous gland function: pathologies or diseases of the auditory organs, such as inflammations or infections, can alter the production and quality of earwax.
- Self-removal of a wax plug: improper removal of a wax plug without professional intervention can compact the plug and complicate its removal.
Possible symptoms of a sulfur plug
Symptoms of the presence of a earwax plug can vary depending on the degree of blockage in the ear canal and individual characteristics of the patient. Some common signs include a feeling of pressure in the ear, temporary or permanent hearing loss, noise or buzzing in the ear (tinnitus), as well as a feeling of fullness in the ear. More serious symptoms may include dizziness, headaches, or even nausea and vomiting if the earwax plug has led to significant impairment of hearing and balance.
Signs indicating the presence of an earwax plug may initially seem quite ordinary; however, their timely recognition and professional examination by a specialist can help prevent possible complications and ensure timely and effective treatment of this condition.
- Feeling of pressure in the ear: Some people may experience a feeling of pressure or blockage in the ear caused by a buildup of wax in the ear canal.
- Hearing deterioration: An earwax blockage obstructing the ear canal can lead to temporary or permanent hearing deterioration.
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ear): The presence of an earwax plug may cause noise or ringing in the ear, known as tinnitus.
- Feeling of ear fullness: Patients with an earwax blockage often describe a sensation of ear fullness, which may be related to the obstruction of the ear canal.
- Dizziness and headache: In some cases, an earwax blockage can cause dizziness, headaches, or even nausea, particularly with significant impairment of hearing and balance.
Approaches to the treatment of sulfur plugs: expert opinions
The expert opinion on the treatment of earwax plugs emphasizes the importance of a professional approach to this condition. Effective treatment methods include gentle rinsing of the ear canal, vacuum removal of the earwax plug, mechanical extraction when necessary, as well as the use of special medications to soften and dissolve the wax. Experts also highlight that self-cleaning of the ears can lead to injuries to the ear canal and compaction of the earwax plug, and recommend consulting qualified specialists for earwax removal procedures.
Modern methods of treating earwax plugs include the use of innovative techniques and equipment, which increases the effectiveness and safety of the procedures. Experts note that an important aspect of treatment is preventing recurrences and regular preventive examinations of the ears for timely identification and removal of earwax plugs. The approach to the treatment of earwax plugs should be individualized and based on an examination of the patient by an otolaryngologist, followed by the necessary procedures to restore hearing function and ensure comfortable ear conditions.

Methods for diagnosing a sulfur plug
Diagnosis of earwax impaction involves a number of methods that help determine the presence and nature of earwax in the ear canal. The doctor may perform a visual examination of the ears, use special tools to inspect the ear canals, or even use specialized devices, such as an otolaryngoscope, for a more detailed study of the situation in the auricle. If earwax impaction is detected, the doctor may also conduct audiometric testing to assess hearing levels and identify possible changes after the removal of the earwax.
Determining the presence of earwax impaction may also require specialized procedures, such as tympanometry to assess the condition of the eardrum, as well as the use of computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to obtain more detailed information about the condition of the ears and the reasons for the formation of earwax impaction. Accurate diagnosis allows for determining the degree of earwax blockage and developing an individual treatment plan aimed at effectively and safely resolving this condition.
- Visual inspection: The doctor conducts an external examination of the ears using a light source and magnifying glass to assess visible signs of the presence of earwax blockage.
- Instrumental examination: The doctor may use special tools, such as an ear probe or forceps, to remove earwax blockage or assess its consistency.
- Audiometric examination: Conducted to evaluate the patient’s hearing and identify any changes after the removal of earwax blockage.
- Tympanometry: A method that allows assessment of the condition of the eardrum and detection of any changes caused by earwax blockage.
- Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): These methods provide more detailed information about the condition of the ear structures and may be used to clarify the diagnosis of earwax blockage.
Methods for treating a sulfur plug
In addition to mechanical removal, in some cases, special solutions are used to soften the earwax plug and facilitate its subsequent extraction. However, it is important to remember that self-removal of the earwax plug using cotton swabs or other objects can lead to injuries of the ear canal and eardrum, so for safe and effective treatment, it is necessary to consult a specialist for professional intervention.
-
– Mechanical removal: This method involves using special tools and equipment for the physical extraction of earwax from the ear canal to restore normal passage of the auditory canal.
– Use of solutions: Some cases of earwax require preliminary softening of the wax using special solutions, which facilitates the subsequent removal of the plug and reduces the risk of damaging the ear canal.
– Irrigation procedures: This method involves flushing the ear canal using a gentle solution to remove accumulated earwax and facilitate its extraction.
– Prescription of ear drops: A doctor may recommend special ear drops that contain ingredients to soften the earwax plug and improve its removal from the ear canal.
– Performing aspiration procedures: Under certain circumstances, an aspiration procedure may be required, in which the plug is removed under the supervision of a doctor using specialized equipment.
Measures for the prevention of sulfur plug
To maintain ear health and prevent earwax plugs, it is important to monitor the humidity level in the ear canal and avoid overcooling. It is also advisable to regularly undergo preventive examinations by an otolaryngologist for the timely identification and treatment of any disorders or pathologies of the auditory apparatus, which can also contribute to the prevention of wax plug formation.
- Regular hygienic cleaning of ears: Clean your ears with gentle products and cotton swabs, avoiding sharp objects to prevent wax buildup.
- Avoiding hypothermia: Maintain normal humidity levels in the ear canal and avoid cooling down, which will help prevent potential wax blockages.
- Regular preventive check-ups with an otorhinolaryngologist: It is important to visit a doctor for the timely detection and treatment of any changes or pathologies in the ear canal, which will help prevent wax blockages.
- Avoiding the use of sharp objects: Do not insert sharp or pointed objects into your ears for cleaning to prevent injury and potential wax buildup.
- Monitor the health of your hearing aid: Maintain ear health by treating any infections or pathologies in a timely manner and consult a specialist if necessary to prevent wax blockages.
Amazing facts about sulfur plugs
In addition, earwax blockage can cause various symptoms, including a feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear, hearing impairment, ringing in the ears, or even dizziness. Failure to address earwax blockages in a timely manner can lead to further complications and deterioration of hearing. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor at the first signs of an earwax blockage for professional diagnosis and treatment.