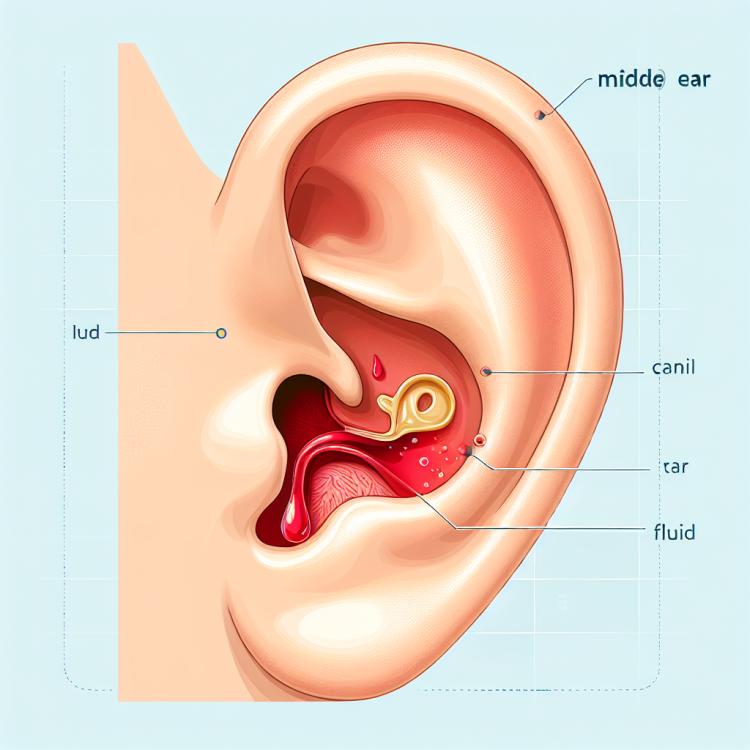
Otitis media: causes, symptoms, and effective treatment methods
- Understanding otitis media: symptoms, causes, and treatment
- Factors contributing to the development of otitis media
- The main signs of acute middle ear otitis.
- Expert opinion on treatment methods for otitis media
- Methods for diagnosing otitis media
- Methods of treating otitis media
- Measures to prevent otitis media
- Fascinating aspects of otitis media
- FAQ
Understanding otitis media: symptoms, causes, and treatment
Acute otitis media, or middle ear inflammation, is an inflammatory disease of the middle ear, most often caused by a bacterial infection. The key symptoms of acute otitis media include ear pain, hearing loss, and the discharge of purulent fluid from the ear canal. Common causes of acute otitis media include respiratory tract viruses, bacteria, and allergies, as well as anatomical features of the ear.
Treatment for middle ear inflammation may include the use of antibiotics for bacterial infection, pain relievers to alleviate pain, and warm compresses. In some cases, a procedure to puncture the eardrum may be required to remove pus from the middle ear. Early diagnosis and proper treatment of middle ear inflammation are important to prevent complications and ensure the patient’s quick recovery.
Factors contributing to the development of otitis media
Otitis media can arise for various reasons, including upper respiratory infections, allergic reactions, anatomical features, changes in atmospheric pressure during flights or dives. Risk factors contributing to the development of otitis media may include regular smoking, the presence of conditions such as allergies or reflux, as well as insufficient control over noise and humidity levels in the environment.
Understanding the main causes of otitis media is crucial for its prevention and effective treatment. Considering the individual characteristics of the patient, it is necessary to prevent exposure to risk factors and to timely implement measures to strengthen the immune system, as well as to follow hygiene measures to prevent ear infections.
- Upper respiratory infections: viruses or bacteria entering the body through the nose or throat can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the middle ear.
- Allergic reactions: allergens such as pollen or dust mites can cause inflammation and swelling of the ear mucosa.
- Regular smoking: exposure to toxic substances in tobacco smoke can contribute to the development of otitis media.
- Changes in atmospheric pressure: sharp changes in pressure, for example during flights or dives, can cause an imbalance in the ear, which contributes to the development of otitis.
- Anatomical features: a narrow nasopharyngeal passage or other anatomical features may contribute to congestion and the development of inflammation in the ear.
The main signs of acute middle ear otitis.
Acute otitis media is often accompanied by acute ear pain that intensifies at night or when chewing. As the condition progresses, a feeling of unpleasant pressure in the ear may arise, sometimes accompanied by hearing problems. Patients also often complain of general malaise, high fever, and possibly the appearance of discharge or reddening of the eardrum.
Studying and recognizing the main signs of acute otitis media is important for timely medical attention and the start of treatment. A detailed examination of the ear’s condition and the detection of characteristic symptoms will help determine the extent and severity of the disease, which in turn will allow for appropriate treatment to be prescribed and prevent possible complications.
- Sharp pain in the ear: patients often experience sharp pain in the ear, which may worsen at night or when chewing.
- Pressure in the ear: a sensation of pressure in the ear may occur with the development of the disease, sometimes accompanied by hearing problems.
- General malaise and high fever: general malaise, weakness, and increased temperature may be characteristic symptoms of acute otitis media.
- Discharge from the ear: sometimes the disease is accompanied by the appearance of discharge or redness of the eardrum.
- Hearing problems: possible hearing impairments may also be one of the main signs of acute otitis media.
Expert opinion on treatment methods for otitis media
Expert opinions on the treatment methods for otitis media highlight the importance of an individualized approach for each patient. Medical center doctors agree that the initial stages of acute otitis media can be successfully alleviated by taking anti-inflammatory medications and local treatment procedures. For more serious cases, where the infection is progressing or there is a high risk of complications, the use of antibiotics or surgical intervention may be necessary.
The medical community also emphasizes the need for monitoring the treatment process and regular monitoring of the patient’s condition. Experts stress that the unique features of each case require an approach based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the extent of disease progression, which underscores the importance of consulting a qualified specialist for effective treatment of otitis media.

Methods for diagnosing otitis media
The diagnosis of otitis media includes an examination by an otolaryngologist, who can visually assess the condition of the eardrum using a special instrument – an otoscope. If necessary, audiometry may be conducted to determine hearing impairments, as well as computed tomography, which helps to see a more detailed picture of changes in the ear. It is important to identify the characteristic signs of inflammation and assess the severity of the disease for the correct choice of treatment methods.
A thorough study of symptoms, conducting objective investigations, and evaluating the results of diagnostic procedures allow for an accurate determination of the cause of otitis media and the necessary steps for treatment. Diagnosis not only enables differential diagnosis of otitis of other etiologies but also identifies the individual characteristics of the patient, which is important for prescribing effective therapy and preventing disease recurrences.
- Doctor’s examination: The otolaryngologist conducts a visual examination of the ear using an otoscope to assess the condition of the eardrum.
- Audiometry: Hearing examination helps to identify hearing function disorders and assess their severity.
- Computed tomography (CT): Conducting a CT of the ear can provide a more detailed view of the structure and changes in the middle ear.
- Additional studies: May include X-rays, endoscopy to evaluate the middle ear cavity, and other methods depending on the necessity in each case.
- Assessment of results: The combination of data from diagnostic procedures helps to identify the cause of otitis and determine the treatment strategy, as well as establish a baseline for monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
Methods of treating otitis media
Each case of acute otitis media requires an individualized approach to treatment, taking into account the patient’s characteristics and the severity of the disease. Effective treatment not only includes alleviative methods but also preventive measures aimed at preventing complications and recurrences of the disease, which will help the patient in quick recovery and restoration of ear function.
- Use of anti-inflammatory medications: The use of medications aimed at reducing inflammation can help alleviate pain and symptoms associated with otitis media.
- Antibiotic therapy: In the case of a bacterial infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to combat pathogenic microorganisms and prevent complications.
- Ear drainage: Procedures such as paracentesis and tympanostomy may be performed to remove exudate from the ear and ensure drainage, which aids recovery.
- Inhalations and compresses: The use of inhalations with antiseptics and warm compresses on the area of the ear can help relieve discomfort and accelerate healing.
- Resting regime compliance: An important element in the treatment of otitis media is rest and avoiding factors that may exacerbate the condition, such as exposure to cold or harmful substances.
Measures to prevent otitis media
Attention should also be paid to ear hygiene, avoiding self-cleaning of the ears with cotton swabs and other sharp objects to prevent damaging the eardrum and creating conditions for infection to develop. Regular ventilation of premises, moderate physical activity, and a balanced diet also help strengthen immunity and reduce the risk of otitis media.
- Proper treatment of infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract: timely and adequate treatment of colds and other respiratory infections helps prevent their spread to the middle ear.
- Avoiding secondhand smoke: tobacco smoke can irritate the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs, increasing the risk of inflammation in the ear and infections.
- Maintaining ear hygiene: avoiding cleaning the ears with sharp objects helps prevent damage to the eardrum and infections.
- Regular ventilation of premises: improves air circulation, preventing moisture buildup and providing a healthier environment for the ears.
- Balanced diet and healthy lifestyle: strengthening the immune system through proper nutrition, moderate physical activity, and avoiding harmful habits reduces the risk of developing otitis media.
Fascinating aspects of otitis media
Moreover, research in the treatment of otitis media allows for the development of more effective treatment methods and identifies new aspects of the interconnection between inflammation in the ear and other processes in the body. Understanding the intriguing details of otitis media not only enhances the treatment procedure itself but also enriches our knowledge of the body’s reactions to infections and inflammation in general.