Stenosing ligamentitis: diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis
- Understanding the essence of stenosing ligamentitis
- Etiology of stenosing ligamentitis
- The clinical picture of stenosing ligamentitis
- Approaches to the treatment of stenosing ligamentitis: expert opinions
- Diagnosis of stenosing ligamentitis
- Treatment of stenosing ligamentitis
- Prevention of stenosing ligamentitis
- Interesting aspects of stenosing ligamentitis
- FAQ
Understanding the essence of stenosing ligamentitis
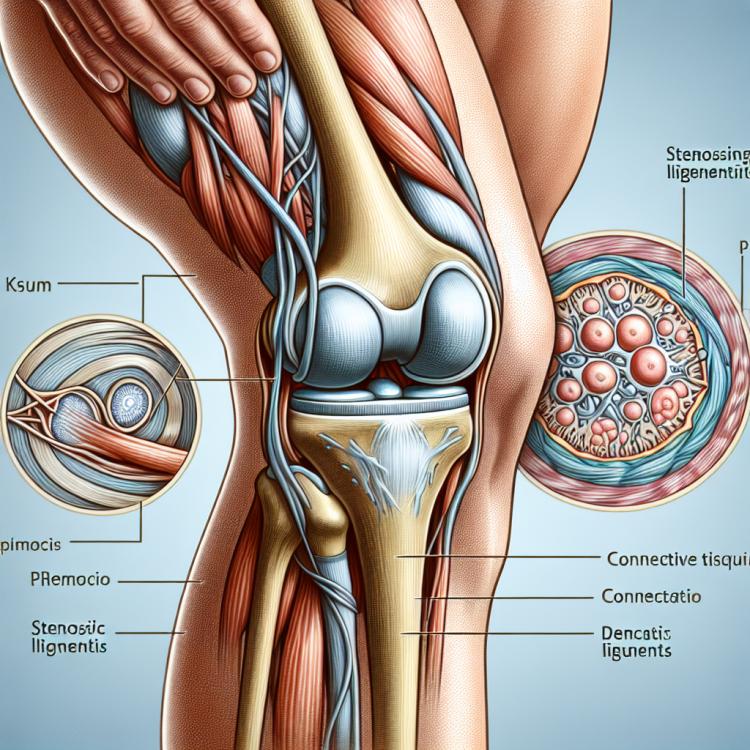
Stenosing ligamentitis is an inflammatory disease characterized by the narrowing of the space around the tendon structures (ligaments), leading to their compression and structural changes. It most commonly affects the tendon structures in the joint areas, resulting in pain, limited mobility, and even dysfunction. This process is caused by damage to the joint tissues, leading to increased pressure within the joint and the formation of adhesions, complicating the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Etiology of stenosing ligamentitis
The etiology of stenosing ligamentitis is due to a complex of factors, including inflammatory processes, degenerative changes, and injuries in the area of the ligaments. Although the precise causes of this condition require further research, it is known that various factors, such as injuries from physical activity, metabolic disorders, and hereditary factors, can contribute to the development of stenosing ligamentitis. Ligaments subjected to mechanical stress or inflammatory processes have an increased risk of developing structural changes, which can lead to stenosis and narrowing of the ligamentous space.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the area of the ligaments can contribute to tissue destruction and the development of stenosis.
- Injuries: Damage and injuries to the ligaments can cause their deformation, leading to stenosis.
- Degenerative changes: Disorders in the structure and function of ligaments due to degenerative changes can be a cause of stenosing ligamentitis.
- Physical load: Excessive or improper physical activity can put additional pressure on the ligaments, causing them to narrow and leading to stenosis.
- Genetic factors: Hereditary predispositions or genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing stenosing ligamentitis.
The clinical picture of stenosing ligamentitis
The clinical picture of stenosing ligamentitis may include various symptoms that manifest depending on the level of damage and the degree of stenosis. Patients may experience pain that worsens with movement or physical activity, limited mobility in affected joints, swelling and puffiness in the area of the affected ligaments, as well as the possible appearance of crepitation during movement. The diagnosis of this condition requires a comprehensive approach, including a clinical examination, joint assessment, and instrumental methods such as X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging to confirm the diagnosis and determine the area of injury.
- Pain and discomfort: Patients may complain of pain in the area of the affected ligaments, which intensifies with movement.
- Restricted mobility: Stenosing ligamentitis may lead to restricted mobility in the joints, making it difficult to perform daily tasks.
- Swelling and puffiness: Swelling and puffiness may be observed at the site of the affected ligaments, related to the inflammatory process.
- Crepitus with movement: During stenosing ligamentitis, crepitus sounds may occur in the affected joints during physical activity.
- Decreased overall mobility: Patients with this condition may experience difficulties in performing movements, which affects overall mobility and quality of life.
Approaches to the treatment of stenosing ligamentitis: expert opinions
The opinions of experts on approaches to treating stenosing ligamentitis may vary depending on the severity of the condition, its progression, and the individual characteristics of the patient. Some specialists prefer a conservative approach, including physiotherapy, rehabilitation, and the use of anti-inflammatory medications, while others may suggest surgical intervention in cases of significant structural damage. The optimal treatment for stenosing ligamentitis can only be determined after careful diagnosis, consideration of all factors, and consultation with specialists to choose the most effective treatment strategy for each specific case.

Diagnosis of stenosing ligamentitis
The diagnosis of stenosing ligamentitis includes various methods aimed at identifying and assessing the condition of the affected ligaments. A clinical examination, including the medical history and physical examination, helps the doctor detect signs of inflammation, pain during movement, and limitations in joint mobility. Instrumental methods, such as X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT), may be used for an accurate diagnosis and to determine the degree of stenosis, allowing visualization of changes in the ligaments and surrounding tissues.
- Clinical examination: The doctor conducts a detailed examination, identifying signs of inflammation, pain, and limitations in joint mobility.
- Medical history: Gathering information about previous injuries, symptoms, and risk factors helps to establish the causes of possible ligament stenosis.
- X-ray: X-rays allow visualization of the condition of the bones and assessment of possible changes in the structure of the joints.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI provides a more detailed image of the ligaments, helping to identify the degree of damage and areas of stenosis.
- Computed tomography (CT): CT may be used for additional visualization of structural changes in the area of the joints and ligaments.
Treatment of stenosing ligamentitis
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Physical therapy and exercises: help improve joint mobility, strengthen muscles, and relieve tension.
- Corticosteroid injections: local injections can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain in affected areas.
- Hyaluronic acid preparations: used to improve the lubricating properties of joints and reduce pain.
- Rehabilitation measures: an important part of treatment for restoring joint function, strengthening muscles, and preventing relapses.
Prevention of stenosing ligamentitis
- Strengthening muscles and ligaments: Regular exercises to strengthen muscles and ligaments help prevent excessive strain on joints and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Proper nutrition: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals contributes to maintaining the health of joints and ligaments.
- Avoiding injuries: Preventing traumatic injuries to the joints by being cautious and using protective gear during sports activities.
- Regular medical check-ups: Visiting a doctor to monitor joint health and timely identify potential problems.
- Training proper movement technique: Proper training and execution of various exercises and movements help avoid overloading and injuries to the joints.