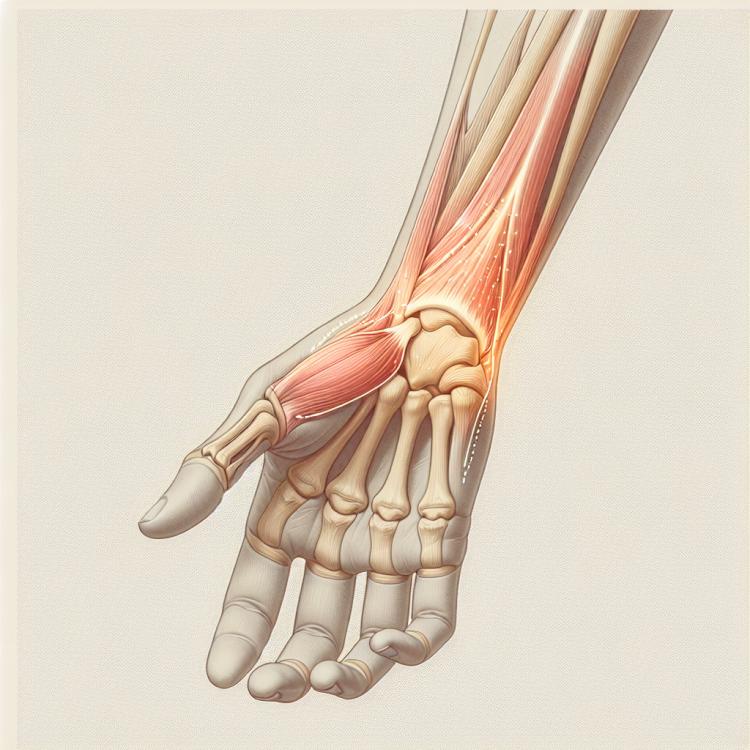
Tendovaginitis: what are the symptoms, causes, and treatment methods?
- Understanding Tendovaginitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
- Etiology of tenosynovitis
- The clinical picture of tenosynovitis
- Expert opinion on the treatment of tenosynovitis
- Methods for diagnosing tenosynovitis
- Strategies for treating tenosynovitis
- Methods of preventing tenosynovitis
- Fascinating aspects of tenosynovitis
- FAQ
Understanding Tendovaginitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Tendovaginitis is an inflammatory condition of the joint capsule, characterized by pain and limited joint mobility. Symptoms include pain and swelling around the affected joint, which worsen with movement. Causes of tendovaginitis can include joint overload, injuries, or infectious processes.
Treatment for tendovaginitis typically involves a combination of rest, ice application, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes surgical intervention. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment play a crucial role in preventing complications and restoring full joint functionality.
Etiology of tenosynovitis
Tendovaginitis is an inflammatory disease characterized by inflammation of the joint sheaths (synovial sheaths) and tendons. Its development is mainly associated with tendon overload, injuries, infectious processes, or rheumatic diseases. The causes of tendovaginitis may also include damage caused by repetitive movements, improper positioning, or load on specific tendons. Various factors, including age, gender, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle, may also play a role in the development of this disease.
- Tendon overload: Excessive loads or repetitive movements can cause inflammation of the tendons.
- Injuries and bruises: Mechanical damage to the tendons can lead to the development of tenosynovitis.
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can cause inflammation of the joint sheaths and tendons.
- Rheumatic diseases: Common rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis can contribute to the development of tenosynovitis.
- Genetic factors: Some hereditary traits may increase the risk of developing inflammatory diseases, including tenosynovitis.
The clinical picture of tenosynovitis
Symptoms of tenosynovitis usually include pain in the area of the affected joint or tendon, swelling, redness of the skin, and limited mobility. In some forms of the disease, crunching and creaking may be observed during movement, as well as possible symptoms of inflammation, such as an increase in temperature of the skin over the affected area.
The diagnosis of tenosynovitis is typically based on clinical manifestations and data from physical examination. Additional instrumental and laboratory studies, such as ultrasound, X-rays, or blood tests for inflammatory markers, are often required to confirm the diagnosis.
- Pain and discomfort: Patients often experience pain when moving the affected joint or tendon, which may intensify with physical activity.
- Swelling and redness: Swelling and redness of the skin around the affected area may be observed due to the body’s inflammatory response.
- Limited mobility: There may be a limitation in the movement of the affected joint or tendon due to pain and inflammation, making ordinary movements difficult.
- Creaking and grinding: In some forms of tendovaginitis, sound effects such as creaking and grinding may occur upon movement, caused by the friction of structures against one another.
- Increased skin temperature: A sensation of warmth and an increase in skin temperature in the area of the affected spot may be a sign of inflammation and the body’s response to the disease.
Expert opinion on the treatment of tenosynovitis
Experts emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to the treatment of tendovaginitis, which usually includes a combination of conservative therapy methods, physiotherapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Conservative methods typically involve the use of anti-inflammatory medications, physiotherapy, rehabilitation, and restriction of physical activity.
Experts also highlight the importance of individualizing treatment, taking into account the characteristics of each clinical case of tendovaginitis. Some patients may require prolonged courses of therapy, while others may need a more active approach with earlier phases of rehabilitation and physical activity.

Methods for diagnosing tenosynovitis
Diagnosis of tenosynovitis includes a number of methods that can be applied to confirm the presence of the disease and determine its characteristics. Clinical examination, including the study of symptoms and physical examination of the affected area, is the first step in the diagnosis of tenosynovitis. Additional instrumental methods, such as ultrasound and X-ray, can be used to visualize the affected tissues and rule out other pathologies.
In addition, laboratory tests, such as blood tests for inflammatory markers, may be conducted to assess the degree of inflammation in the body. It is important to consider that proper diagnosis of tenosynovitis plays a key role in determining the treatment strategy and preventing possible complications.
- Clinical examination: identification of characteristic symptoms and conducting a physical examination of the affected area.
- Ultrasound examination: visualization of the affected tissues of tenosynovitis to clarify the diagnosis.
- X-ray: a method of examination that can be used to exclude other pathologies and assess the condition of the bones in the area of injury.
- Laboratory studies: include blood tests for inflammatory markers, which help assess the degree of inflammation and the general condition of the body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a more detailed and accurate method of visualizing the affected tissues for diagnosing tenosynovitis in complex cases.
Strategies for treating tenosynovitis
In cases where conservative methods do not have the desired effect, surgical intervention may be required. Surgical treatment of tenosynovitis may involve the removal of inflamed tissue, restructuring of tendons, or rehabilitation of joints. The optimal treatment method is chosen based on the severity of the disease, individual characteristics of the patient, and specialist recommendations.
- Conservative treatment: Includes rest, ice application, physiotherapeutic procedures, and rehabilitation exercises to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Use of medications to reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area may be possible.
- Corticosteroid injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and pain in the tendons and joints.
- Physiotherapy: A set of exercises and physical therapy procedures can help strengthen muscles, improve mobility, and restore affected tissues.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where conservative methods have not yielded results, surgery may be required to address the problem, such as removing inflamed tissue or rehabilitating tendons and joints.
Methods of preventing tenosynovitis
Another important aspect of tenosynovitis prevention is proper handling of joints and tendons in daily activities. This includes using the correct technique when lifting weights, avoiding sudden movements, as well as taking regular breaks and doing stretching exercises during long periods of static positions. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding harmful habits, also contributes to the prevention of tenosynovitis.
- Regular exercise: Exercises to strengthen muscles and tendons help prevent overloads and tendon injuries.
- Correct posture and movement technique: Maintaining correct posture and technique while working and exercising helps avoid excessive strain on the tendons.
- Regular breaks and warm-up exercises: Regular breaks and warm-up exercises help reduce tension in the muscles and tendons during prolonged periods of static positions.
- Proper care of joints and tendons: Avoiding sudden movements, proper weight lifting technique, and caring for joints contribute to preventing injuries and overloads of the tendons.
- Healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding bad habits, and regular physical activity help maintain the health of the joints and tendons.
Fascinating aspects of tenosynovitis
Interestingly, tenosynovitis can occur not only in athletes or individuals with increased physical activity but also in those leading a sedentary lifestyle. This pathology demonstrates the importance of moderation in physical activity and a careful approach to maintaining the health of joints and tendons in everyday life.