Knee joint injuries: diagnosis, treatment methods, and prevention
- Basics of knee joint injuries
- Etiology of knee joint injuries
- Clinical picture of knee joint injuries
- Expert opinion on the treatment of knee joint injuries.
- Methods for diagnosing knee joint injuries
- Approaches to the treatment of knee joint injuries
- Prevention of knee joint injuries
- Amazing facts about knee joint injuries
- FAQ
Basics of knee joint injuries
The basics of knee joint injuries include a variety of damage types, such as ligament strains, cartilage injuries, bone fractures, and meniscus tears. The knee joint, being one of the largest and most injury-prone joints in the body, requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. Recovery of knee joint function after injuries demands precise diagnosis, individualized selection of treatment and rehabilitation methods, as well as adherence to recommendations for the prevention of possible complications.
Etiology of knee joint injuries
Knee joint injuries can occur due to various reasons, including traumatic incidents, sports injuries, or damage related to everyday activities. One of the main mechanisms is a knee injury resulting from a direct blow to the outside or inside of the knee, which can lead to damage to various structures of the joint, such as cartilage and ligaments. Other causes of knee joint injuries may include improper exercise techniques, overload and excessive tension on the knee, as well as a predisposition to joint problems due to anatomical features or previous injuries.
It is important to consider the factors that contribute to knee joint injuries in order to take measures to prevent them. Ensuring proper exercise techniques, strengthening the muscles and ligaments around the knee, and using appropriate protective gear when engaging in sports or physical activities can reduce the risk of injuries and maintain the health of the knee joint.
- Traumatic situations: direct blows, falls, car accidents, and other external impacts can lead to damage to the knee joint.
- Sports injuries: high loads, unsuccessful movements, or traumatic situations in sports can cause various knee injuries.
- Incorrect exercise technique: improperly performed exercises can create incorrect loads on the knee, increasing the risk of injury.
- Overload and excessive tension: excessive loads on the knee joint without sufficient time for recovery can cause damage to the tissues and structures of the joint.
- Anatomical features and predisposition: certain anatomical features of the knee joint may predispose to injuries, and previous injuries may increase the risk of new traumatic conditions.
Clinical picture of knee joint injuries
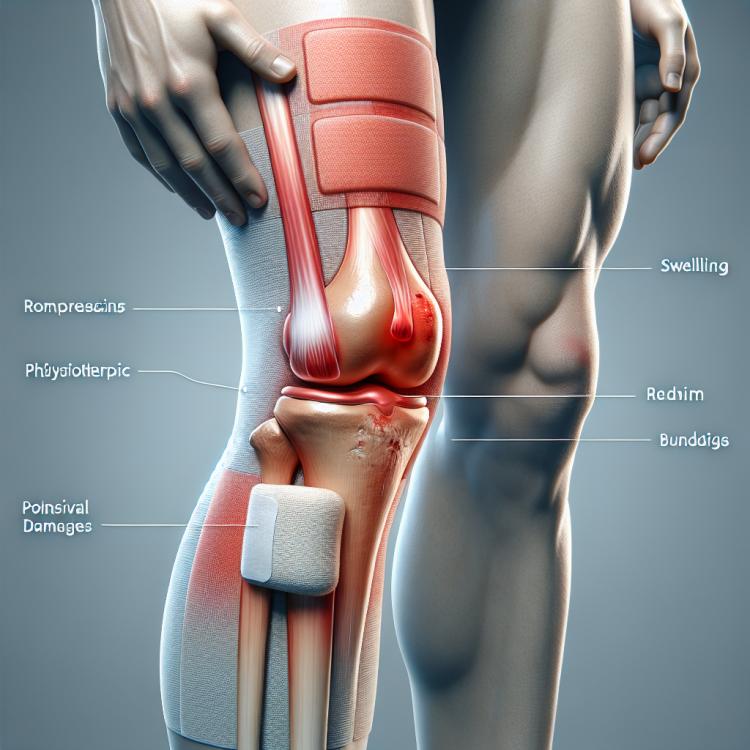
The clinical picture of knee joint injuries can manifest with various symptoms, including swelling and tenderness in the knee area. Patients may experience limited mobility in the knee, a feeling of instability or catching, as well as weakness in the leg when attempting to load the knee joint. In addition, knee injuries often present symptoms such as bruising, skin redness, or the characteristic creaking or cracking noise when moving the knee joint.
It is important to pay attention to early signs of knee joint injury, such as changes in the knee structure, unusual sensations during movements, or the appearance of pain when bearing weight. Early medical attention and precise diagnostic examination allow for timely identification of knee joint injuries and the initiation of appropriate treatment to prevent complications and facilitate the rapid recovery of joint function.
- Swelling and tenderness: knee joint injury is often accompanied by swelling and a feeling of pain in the joint area.
- Limited mobility: patients may experience difficulty in moving the knee due to the injury, which manifests as limited mobility.
- Feeling of instability: those affected may feel instability in the knee or a sensation of the joint “popping out” due to ligament damage.
- Weakness in the leg: with knee damage, patients may experience weakness in the leg, especially when trying to load the joint.
- Bruising and redness of the skin: the appearance of bruises or redness around the knee may be a consequence of knee joint injury.
Expert opinion on the treatment of knee joint injuries.
Experts in orthopedics and traumatology emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to the treatment of knee joint injuries, which includes conservative and surgical methods, physiotherapy, rehabilitation, and postoperative monitoring. Individualizing therapy based on the type and degree of injury, as well as patient characteristics, plays a key role in the successful treatment and recovery of knee joint functions.
Experts highlight the significance of early treatment of knee joint injuries to prevent complications and minimize consequences. Effective management of pain syndrome, restoration of knee joint mobility, strengthening of joint structures, and a gradual return to daily activities, taking into account the individual needs of the patient, contribute to the optimal outcome in the treatment of knee joint injuries.

Methods for diagnosing knee joint injuries
The diagnosis of knee joint injuries involves a variety of medical examination methods to achieve an accurate diagnosis. Experts may use clinical methods such as taking a medical history and physical examination to assess the extent of knee joint damage. For a more detailed evaluation, additional research methods may be employed, including radiography, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), or CT (computed tomography), which allow for visualization of the joint structures and identification of possible injuries.
The use of modern diagnostic methods enables specialists to obtain a complete picture of the knee joint injury, determine the nature of the damage, and develop the most effective treatment plan. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for prescribing appropriate therapy, minimizing the risk of complications, and ensuring successful recovery of knee joint function.
-
– **Clinical examination:** The doctor examines the knee, assesses the degree of swelling, tenderness, changes in the contours of the knee, as well as the joint function.
– **X-ray:** X-rays allow visualization of the bone structures of the joint and detect injuries, fractures, deformities, or anomalies that may cause pain.
– **Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):** MRI helps to see a more detailed image of soft tissues, including cartilage, ligaments, tendons, bones, and other structures of the knee joint, allowing for a more precise assessment of damage.
– **Computed Tomography (CT):** CT provides detailed images of the internal structures of the joint, helping to identify fractures, deformities, and other pathological changes.
– **Arthroscopy:** This is an invasive procedure where the doctor uses a thin tube with a camera to view the internal structures of the knee joint, and it also allows for some surgical interventions and diagnostic procedures.
Approaches to the treatment of knee joint injuries
- Conservative treatment methods: Include rest, application of ice, limitation of physical activity to reduce inflammation and pain, as well as the use of medications to alleviate symptoms.
- Physical therapy: Involves therapeutic exercises, massage, ultrasound therapy, and electrical stimulation to strengthen muscles, restore mobility, and improve circulation.
- Use of orthoses and bandages: Wearing special devices helps to stabilize the joint, reduce the load on damaged tissues, and facilitate the healing process.
- Surgical treatment: May involve ligament reconstruction, cartilage reconstruction, arthroscopy to remove damaged tissues, or other surgical procedures depending on the nature of the injury.
- Rehabilitation: After the main treatment, it is important to carry out rehabilitation activities, including physical therapy, therapeutic exercise sessions, and gradual return to an active life for complete restoration of knee joint function.
Prevention of knee joint injuries
To prevent knee joint injuries, it is also important to monitor your overall health and manage your weight, as excess weight increases the load on the joint and raises the likelihood of injury. A balanced diet, which includes an adequate amount of nutrients and minerals, contributes to strengthening the joint tissues and reducing the risk of damage. Regular medical check-ups and timely treatment of possible knee joint issues are also important aspects of injury prevention.
- Strengthening the muscles: Regular exercises to develop strength and flexibility in the muscles surrounding the knee joint help improve its stability and protect against injuries.
- Correct movement technique: Training and adhering to proper techniques for performing exercises and sports movements reduces the risk of knee injuries during physical activity.
- Use of protective gear: Wearing knee pads and other protection when engaging in sports helps prevent impacts and injuries to the knee joint.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Weight control, healthy eating, adequate fluid intake, and regular physical exercise contribute to the overall strengthening of the body and joint health.
- Regular medical check-ups: Timely identification and treatment of possible knee joint issues help maintain its health and prevent injuries.
Amazing facts about knee joint injuries
Another remarkable fact is that modern medicine is continually improving methods for diagnosing and treating knee injuries, allowing for a more accurate determination of the nature of the damage and offering individualized approaches to restoring joint function. It is also important to note that the prevention of knee injuries, which includes strengthening the muscular corset, proper technique in performing exercises, and wearing protective gear, plays a key role in reducing the risk of various injuries and maintaining joint health throughout life.