Tubootitis (eustachitis): causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
- Definition and main characteristics of tubo-otitis (eustachitis)
- Etiology of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Symptoms of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Expert Opinions on the Treatment of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Diagnostic Approach for Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Management of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Prevention of Tubotitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Fascinating Facts About Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- FAQ
Definition and main characteristics of tubo-otitis (eustachitis)
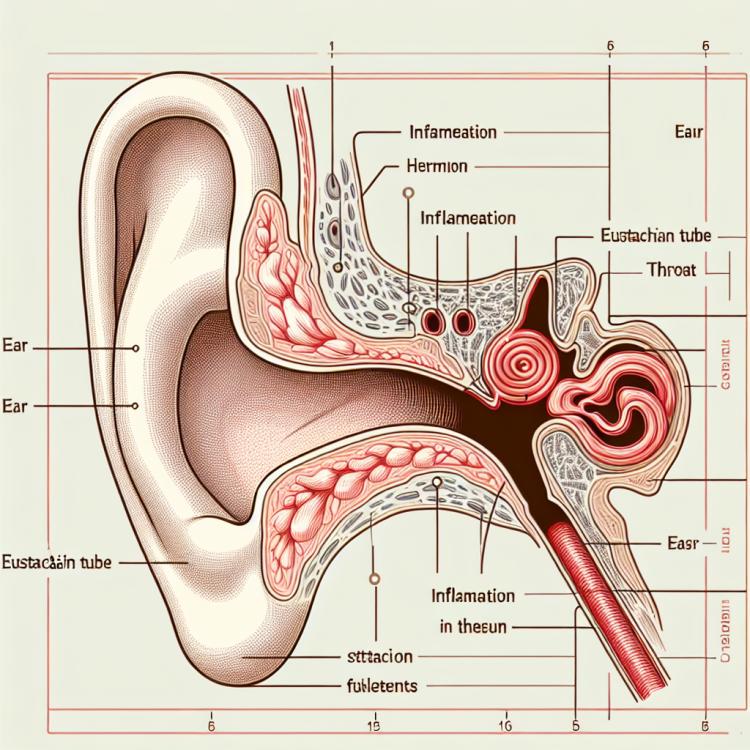
Tubootitis, also known as Eustachitis, is an inflammatory disease of the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the throat. The key characteristics of tubootitis are itching in the ear, pain and congestion in the ears, as well as hearing impairment. During an exacerbation of the disease, there may be an absence of discharge from the ear and an increase in body temperature.
The mechanism of tubootitis development is usually associated with infection, allergic reactions, or dysfunction of the Eustachian tube. Treatment for this condition may include the use of anti-inflammatory medications, topical agents for the nose and throat, physiotherapy procedures, and, in some cases, antibacterial medications.
Etiology of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Etiology of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) includes a variety of factors. Acute tubootitis is commonly caused by viral upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold, which lead to inflammation and blockage of the Eustachian tube. Chronic or recurrent cases may be attributed to allergies, nasal polyps, chronic sinusitis, or anatomical variations in the Eustachian tube. Dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can also be a result of sudden changes in barometric pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, leading to barotrauma.
Other factors contributing to tubootitis can include smoking, exposure to environmental irritants, immune system disorders, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In children, enlarged adenoids are a common cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Understanding the underlying causes of tubootitis is essential for appropriate diagnosis and management of this condition, as addressing the root cause can lead to effective treatment strategies and symptom relief.
- Viral infections: One of the common causes of tubo-otitis is viral respiratory infections, which lead to inflammation and blockage of the Eustachian tube.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can contribute to the development of long-lasting or recurring tubo-otitis.
- Anatomical features: Variations in the structure of the Eustachian tube can lead to its dysfunction.
- Smoking and environmental exposure: Smoking and contact with environmental irritants can worsen the function of the Eustachian tube.
- Systemic diseases: Some systemic diseases, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or immune system disorders, can contribute to the development of tubo-otitis.
Symptoms of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Симптомы тубоотита (дисфункция евстахиевой трубы) могут варьироваться в зависимости от степени тяжести и продолжительности состояния. Пациенты могут испытывать боль в ухе, давление или ощущение заложенности из-за нарушенной вентиляции среднего уха. Потеря слуха или глухота также могут возникать в результате дисфункции евстахиевой трубы, что влияет на передачу звуковых волн во внутреннее ухо.
Кроме того, пациенты с тубоотитом могут жаловаться на тиннитус, который характеризуется звоном или жужжанием в ушах. Некоторые люди могут сообщать о головокружении или вертиго, особенно если дисфункция связана с нарушениями во внутреннем ухе. Наличие повторяющихся ушных инфекций или накопления жидкости за барабанной перепонкой может дополнительно способствовать симптоматике тубоотита. Понимание этих признаков и симптомов имеет важное значение для точной диагностики и лечения дисфункции евстахиевой трубы.
- Боль в ухе: У пациентов с тубоотитом может ощущаться острая или тупая боль в пораженном ухе, часто описываемая как ноющая или пульсирующая.
- Чувство давления: Распространенный симптом дисфункции евстахиевой трубы – это ощущение давления или полноты в ухе, похожее на чувство заблокированного или закупоренного уха.
- Трудности со слухом: Нарушение вентиляции среднего уха может привести к потере слуха, глухим звукам или ощущению снижения слуховой остроты.
- Шум в ушах: Звон, жужжание или другие аномальные звуки в ухе, известные как шум в ушах, могут присутствовать у людей с тубоотитом.
- Головокружение или вертиго: Некоторые пациенты могут испытывать вращающееся сенсацию (вертиго) или легкое головокружение как симптом дисфункции евстахиевой трубы, особенно если задействованы нарушения внутреннего уха.
Expert Opinions on the Treatment of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Expert opinions on the treatment of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) emphasize a multi-faceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific condition. Specialists often recommend initial conservative methods such as nasal decongestants, antihistamines, and nasal corticosteroid sprays to alleviate nasal congestion and reduce Eustachian tube inflammation. Additionally, experts highlight the importance of addressing underlying factors like allergic rhinitis or sinus infections to prevent recurrent Eustachian tube dysfunction.
In cases where conservative measures are ineffective, experts may consider more advanced interventions such as tympanostomy tube placement to facilitate middle ear ventilation or surgical procedures to correct anatomical abnormalities. Collaboration among otolaryngologists, allergists, and other healthcare providers ensures comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plans for individuals with Tubootitis, aligning with the current evidence-based practices to optimize patient outcomes.

Diagnostic Approach for Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
The diagnostic approach for Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) involves a thorough clinical evaluation to assess the patient’s medical history and presenting symptoms. Otoscopy may reveal signs of inflammation or fluid behind the eardrum, indicating Eustachian tube dysfunction. Audiometric tests, such as tympanometry and pure tone audiometry, can help assess middle ear function and detect any associated hearing loss.
In some cases, imaging studies like computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized to evaluate the anatomy of the Eustachian tube and surrounding structures. Tympanocentesis, a procedure where fluid is extracted from the middle ear for analysis, may be performed to confirm the presence of infection. The diagnostic process aims to accurately identify the underlying cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction, guiding the selection of appropriate treatment strategies for the individual patient.
- Clinical Evaluation: Assessment of medical history and symptoms to identify potential causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Otoscopy: Examination of the ear canal and eardrum for signs of inflammation, fluid, or structural abnormalities indicative of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Audiometric Tests: Utilization of tympanometry and pure tone audiometry to evaluate middle ear function and detect any associated hearing loss.
- Imaging Studies: Consideration of computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the Eustachian tube and related anatomical structures.
- Tympanocentesis: In some cases, extraction of middle ear fluid for analysis may be performed to confirm the presence of infection as a potential cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Management of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
В случаях, когда дисфункция евстахиевой трубы сохраняется или имеет рецидивирующий характер, могут рассматриваться дальнейшие медицинские вмешательства, такие как установка тимпаностомических трубок для облегчения вентиляции и дренажа среднего уха. Антибиотики могут быть прописаны в случае острого среднего отита или вторичных ушных инфекций. Хирургические методы, такие как процедуры дилатации евстахиевой трубы, могут быть показаны в рефракторных случаях. Выбор методов лечения подбирается индивидуально для каждого пациента в зависимости от основной причины, тяжести симптомов и реакции на первоначальную терапию.
- Консервативные меры: Техники, такие как глотание, зевание или маневр Вальсальвы, могут способствовать открытию евстахиевой трубы.
- Назальные деконгестанты: Использование назальных деконгестантов или кортикостероидных назальных спреев может помочь уменьшить nasal congestion и воспаление, улучшая функцию евстахиевой трубы.
- Тимпаностомические трубки: Установка тимпаностомических трубок может быть рассмотрена в случаях стойкой или рецидивирующей дисфункции евстахиевой трубы для улучшения вентиляции и дренажа среднего уха.
- Антибиотики: Антибиотики могут быть назначены для лечения острого среднего отита или вторичных инфекций уха, связанных с дисфункцией евстахиевой трубы.
- Хирургические вмешательства: Для упорных случаев могут быть рекомендованы хирургические варианты, такие как процедуры дилатации евстахиевой трубы, чтобы устранить стойкую дисфункцию евстахиевой трубы.
Prevention of Tubotitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Практика правильных техник для выравнивания давления в ушах во время авиаперелетов, подводного плавания или резких изменений высоты может помочь предотвратить баротравму и последующую дисфункцию евстахиевой трубы. Кроме того, своевременное лечение инфекций верхних дыхательных путей и оперативное управление такими состояниями, как аллергии, синусит или гипертрофия аденоидов, могут помочь предотвратить осложнения, которые могут привести к дисфункции евстахиевой трубы. Образование о факторах риска и раннее распознавание симптомов могут дать возможность людям предпринимать проактивные меры по предотвращению тубоотита.
- Nasal Hygiene: Maintain good nasal hygiene by avoiding allergens and irritants, regular nasal saline irrigation, and treating nasal conditions promptly to prevent congestion and inflammation affecting Eustachian tube function.
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking and minimize exposure to environmental pollutants to reduce the risk of Eustachian tube dysfunction and associated complications.
- Ear Pressure Equalization Techniques: Learn and practice proper techniques to equalize ear pressure during activities like air travel, scuba diving, or rapid altitude changes to prevent barotrauma and Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Prompt Treatment of Infections: Early recognition and timely management of upper respiratory infections can help prevent complications that may lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Education and Awareness: Educate individuals about risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures for Tubootitis to empower them to take proactive steps in maintaining ear health and preventing Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Fascinating Facts About Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Кроме того, определенные факторы риска, такие как курение, аллергии и анатомические вариации в евстахиевой трубе, могут предрасполагать людей к дисфункции евстахиевой трубы. Понимание основных причин и факторов риска, связанных с тубоотитом, имеет важное значение для точной диагностики и индивидуализированных стратегий лечения. Исследования продолжают изучать инновационные подходы к управлению и предотвращению дисфункции евстахиевой трубы, подчеркивая важность постоянных достижений в оториноларингологии и здоровье ушей.
FAQ
Common risk factors associated with Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) include:
1. **Allergies** – Conditions like hay fever can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and affect the Eustachian tube.
2. **Upper respiratory infections** – Colds and sinus infections can lead to swelling and blockage of the Eustachian tube.
3. **Environmental irritants** – Exposure to smoke, pollution, or other irritants can contribute to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
4. **Anatomical abnormalities** – Some individuals may have structural issues, such as a cleft palate, that affect the function of the Eustachian tube.
5. **Age** – Children are more prone to Eustachian tube dysfunction due to the horizontal position of their Eustachian tubes and their susceptibility to infections.
6. **Altitude changes** – Rapid altitude changes, such as during flying or driving in mountainous areas, can lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
7. **Chronic nasal congestion** – Conditions that cause prolonged nasal congestion can also lead to dysfunction of the Eustachian tubes.
8. **Sinus issues** – Chronic sinusitis can lead to persistent inflammation that affects the Eustachian tube.
Understanding these risk factors can help in preventing and managing Tubootitis effectively.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) plays a significant role in the development of otitis media, particularly in children. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and helps to equalize pressure, drain fluid, and protect the middle ear from pathogens.
In children, the Eustachian tube is shorter, more horizontal, and more flexible compared to adults, making it more prone to dysfunction. When the Eustachian tube does not open or close properly, it can lead to several issues:
1. **Pressure Imbalance**: Inability to equalize pressure can cause discomfort and lead to fluid accumulation in the middle ear.
2. **Fluid Accumulation**: Blocked Eustachian tubes can prevent normal drainage of fluid from the middle ear, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
3. **Increased Infection Risk**: With fluid buildup, the risk of developing infections increases due to the presence of pathogens, leading to otitis media.
4. **Reduced Ventilation**: Poor ventilation of the middle ear space can lead to negative pressure, which further contributes to fluid retention and infection.
Overall, the dysfunction of the Eustachian tube contributes to a cycle of fluid buildup and infection, making otitis media a common problem in pediatric populations.
Eustachian tube dysfunction can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and daily activities in several ways. It can cause discomfort and pressure in the ears, leading to pain and difficulty hearing. This may affect communication, making it challenging to participate in conversations or focus in settings like meetings or social gatherings.
Additionally, symptoms such as tinnitus (ringing in the ears), dizziness, or balance issues can hinder routine tasks and reduce overall productivity. Individuals may experience sleep disturbances due to discomfort, further affecting their physical and mental well-being.
In some cases, Eustachian tube dysfunction can lead to recurrent ear infections, which may require medical treatment, adding to the stress and hassle of managing one’s health. Overall, the combination of physical discomfort and the impact on social and work-related activities can diminish an individual’s quality of life.