Tinnitus: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods
- Understanding ear noise (tinnitus)
- Factors causing ear noise (tinnitus)
- The main symptoms of tinnitus (ear noise)
- The specialists’ perspective on tinnitus treatment methods
- Methods for diagnosing tinnitus (ear noise)
- Methods for treating ear noise (tinnitus)
- Measures to prevent ear noise (tinnitus)
- Interesting aspects of tinnitus (ear noise)
- FAQ
Understanding ear noise (tinnitus)
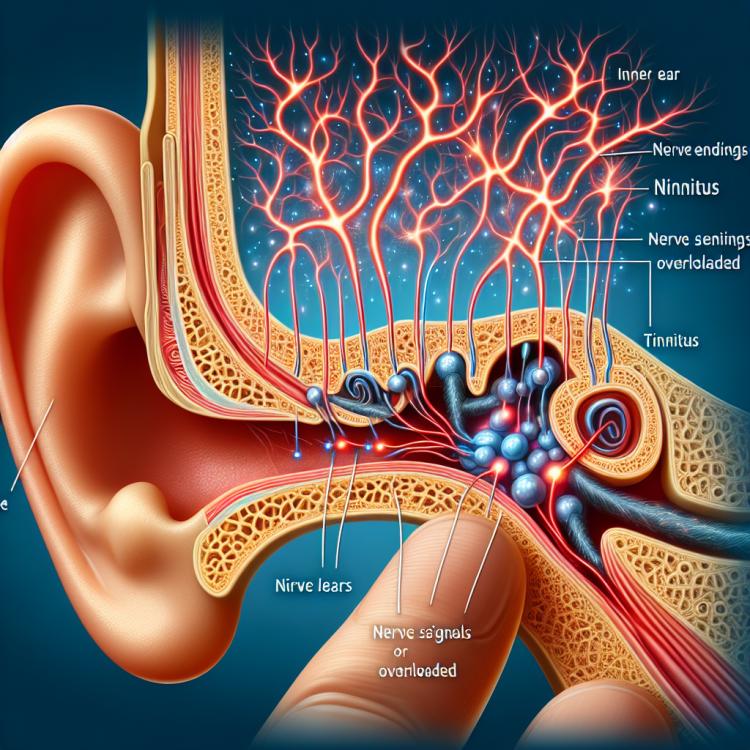
Tinnitus, known as ear noise, is the perception of sound signaling in the absence of external sound sources. This phenomenon is often described as buzzing, hissing, or ringing and can arise due to various causes, including damage to the auditory system, neurological disorders, or cardiovascular issues. Understanding tinnitus involves studying its etiology, pathophysiology, and diagnostic methods, enabling the development of effective treatment strategies to improve patients’ quality of life.
Factors causing ear noise (tinnitus)
Tinnitus, or ear noise, can be caused by various factors, including age-related changes in the auditory system, noise trauma, circulation disorders in the ear, as well as certain diseases such as inner ear diseases, autoimmune diseases, and ear tumors. Tinnitus is especially common among people who have been exposed to prolonged noise or suffer from blood flow disorders in the ear, which can lead to irritation of the auditory nerves and the onset of ear noise.
- Age-related changes in the auditory system: With age, ears may undergo changes that contribute to the development of tinnitus.
- Noise trauma: Continuous or intense exposure to noise can cause damage to the auditory system.
- Inner ear diseases: Various diseases, such as vestibular disorders or inflammations, can be the cause of ear noise.
- Autoimmune diseases: Autoimmune reactions can affect the hearing apparatus, causing tinnitus.
- Ear tumors: The presence of tumors in the ear area can press on blood vessels and nerves, which may be accompanied by ear noise.
The main symptoms of tinnitus (ear noise)
Tinnitus, or ear noise, can manifest in various ways, including sounds of hissing, buzzing, humming, or pulsing in the ears. Patients often describe it as a sound that does not originate from external sources and is felt in one or both ears. The symptoms of tinnitus can be temporary or permanent, and they may vary in intensity and character depending on the cause and the presence of accompanying conditions.
Often, patients with tinnitus also experience other symptoms such as dizziness, ear pain, changes in hearing, and anxiety. It is important to pay attention to such signs and promptly consult a doctor for diagnosis and to determine the optimal treatment.
- Sounds of noise: Tinnitus manifests as various sounds such as hissing, ringing, buzzing, or pulsation.
- Sensation in the ears: Patients perceive tinnitus as a sound originating from within the ear rather than from outside.
- Changes in intensity: The symptoms of tinnitus can vary in intensity and frequency depending on the cause and accompanying factors.
- Duration: Ear noise can be temporary or long-lasting, occurring as single episodes or appearing constantly.
- Accompanying symptoms: Patients with tinnitus often complain of dizziness, ear pain, hearing changes, and other disorders.
The specialists’ perspective on tinnitus treatment methods
Expert opinions on the treatment of tinnitus often emphasize the importance of an individualized approach to patients. Specialists recommend modern treatment methods, including sound therapy, behavioral therapy, medication, and even surgical interventions in certain cases. Experts also highlight the need to reduce stress and improve the patient’s lifestyle to lessen the impact of tinnitus.
With a broad arsenal of treatment methods and extensive experience working with patients with tinnitus, experts recommend a comprehensive approach that includes not only medication but also psychotherapy and rehabilitation. It is important for specialists to take into account the individual characteristics of each patient to find the optimal treatment plan aimed at reducing the level of tinnitus and improving quality of life.

Methods for diagnosing tinnitus (ear noise)
The diagnosis of tinnitus includes taking a medical history and conducting a physical examination of the patient. It is important to consider all associated symptoms, the duration and frequency of the ear noise, as well as the factors that contribute to its exacerbation. During the diagnostic process, specialized studies may be required, including audiometry to assess hearing, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging to identify possible organic causes of tinnitus.
To accurately establish a diagnosis and choose the most effective method of treating tinnitus, it is important to carry out all necessary diagnostic procedures under the guidance of qualified specialists. Given the multitude of possible causes of ear noise, thorough diagnostics will help identify specific factors underlying the development of this symptom and allow for the development of an individualized treatment plan for each patient.
- Collection of medical history and physical examination: Includes discussion with the patient about the nature of the ear noise and its accompanying symptoms, as well as an examination of the ears and surrounding areas to identify possible causes of tinnitus.
- Audiometry: This test allows for the assessment of hearing and identification of sound perception disorders that may be associated with ear noise.
- Computer tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Conducted to identify organic pathologies such as tumors or other anomalies that may cause tinnitus.
- Ear endoscopy: An examination that allows for a detailed study of the condition of the ear canal and detection of possible changes in the ear cavity.
- Vascular examination: Additional methods, such as duplex scanning and angiography, may be used to assess blood vessels in the area of the ear and exclude circulation problems as a possible cause of tinnitus.
Methods for treating ear noise (tinnitus)
It is important to consider the individual characteristics of each patient when choosing the method of tinnitus treatment. The effectiveness of certain methods may vary depending on the nature of the tinnitus and its causes, so consulting a specialized doctor for advice and developing a personalized treatment plan is an important step in managing this condition.
- Medications: The use of drugs may be aimed at improving blood circulation in the inner ear or reducing inflammation if it is the cause of tinnitus.
- Sound therapy: A method based on providing background sounds to distract from ear noise and training the brain to minimize its perception.
- Psychotherapy and behavioral techniques: Help patients learn to cope with stress and anxiety related to tinnitus, which can improve their well-being.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and manipulations aimed at improving circulation and reducing tension in the neck and head areas may help with tinnitus symptoms.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, if tinnitus is caused by structural problems, surgery may be required to improve symptoms.
Measures to prevent ear noise (tinnitus)
It is also important to avoid prolonged exposure to noisy environments without protection and to monitor hearing status, especially for individuals at increased risk of developing ear noise. If the first signs of hearing impairment or ear noise occur, it is necessary to seek medical assistance immediately for timely identification of the causes and provision of the necessary treatment.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular physical exercise, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking.
- Protecting hearing from harmful effects: Avoid prolonged exposure to noisy environments without protection or at high noise levels; use headphones or ear protection when working in a noisy environment.
- Monitoring blood pressure: Regularly monitor your blood pressure, as high blood pressure may contribute to the development of tinnitus.
- Caring for your hearing: Pay attention to your hearing, avoid overloading your ears, do not use loud music in headphones, and avoid direct exposure to noise on the ear.
- Regular medical check-ups: Have regular check-ups with an ear, nose, and throat doctor to detect possible hearing issues early and prevent the development of tinnitus.
Interesting aspects of tinnitus (ear noise)
Another interesting aspect of tinnitus is its impact on the psychological state of patients. The constant presence of unclear noise or sound in the ears can cause anxiety, apprehension, and even depression in some individuals. It is important to take this influence into account when developing treatment methods and supporting patients with tinnitus, as well as continuing research for a deeper understanding of this phenomenon.