Vaginal fistula: diagnosis, complications, and treatment methods
- Explanation of vaginal fistula
- Etiology of vaginal fistula
- Signs of a vaginal fistula
- Approach to the treatment of vaginal fistula: specialists’ opinions
- Methods for diagnosing a vaginal fistula
- Methods for treating vaginal fistula
- Prevention measures for vaginal fistula
- Interesting aspects of treating a vaginal fistula
- FAQ
Explanation of vaginal fistula
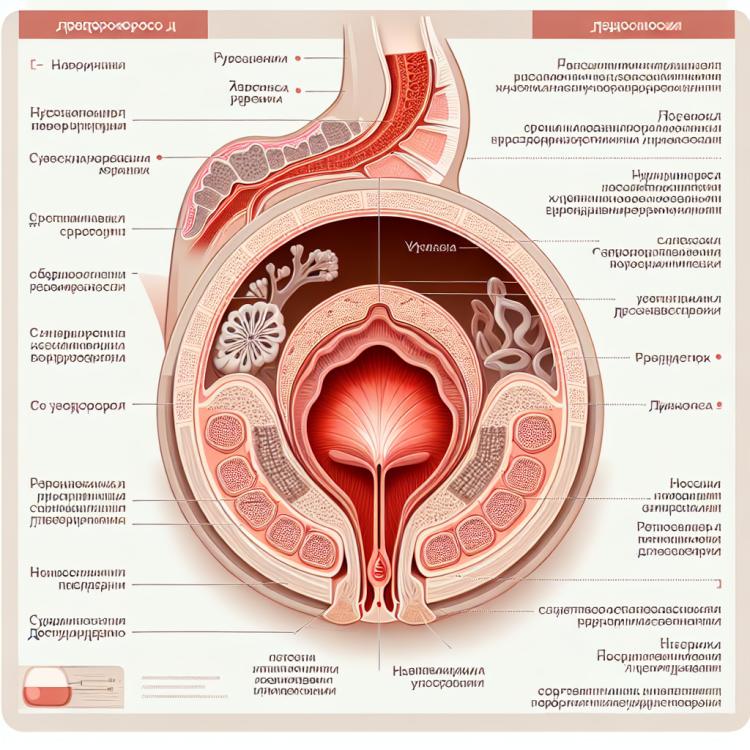
A vaginal fistula is a pathological condition characterized by an unnatural opening between the vagina and other sexual or non-sexual organs, such as the bladder or rectum. This defect can arise from various causes, including trauma during childbirth, surgeries on the uterus, infections, or malignant tumors. Symptoms of a vaginal fistula may include an unpleasant odor, urinary incontinence, vaginal discharge, and increased sensitivity of the vagina to irritants.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of a vaginal fistula are of significant clinical importance, as neglecting this condition can lead to complications such as inflammation, infections, and even sexual dysfunction. Surgical methods for correcting the fistula, including repair or reconstructive surgery, are the primary means of treating this condition, but sometimes conservative treatment using medications and procedures may be necessary.
Etiology of vaginal fistula
Vaginal fistula can arise from a variety of causes, including complications after childbirth, surgical interventions, inflammatory processes, or cancerous tumors in the pelvic area. Tissue damage can lead to the formation of a fistula between the vagina and the bladder, rectum, or other organs, resulting in the undesirable transfer of content between these cavities.
The etiology of vaginal fistula is extensive and includes factors such as perinatal complications, surgical errors, infections, malignant diseases, radiation, as well as injuries from accidents. Proper identification and treatment of the underlying cause are important steps in managing patients with vaginal fistula.
- Consequences of childbirth: traumatic childbirth may lead to damage to the tissues of the vagina and fetal structures.
- Surgical interventions: errors during operations on the pelvic organs can cause the development of a vaginal fistula.
- Inflammatory processes: chronic infections or inflammations can lead to tissue destruction and the formation of fistulas.
- Cancerous tumors: tumor processes in the pelvic region can cause damage to surrounding tissues and the formation of fistulas.
- Radiation and chemotherapy: treatment of cancer of the pelvic organs with radiation or chemotherapy can be a cause of the development of a vaginal fistula.
Signs of a vaginal fistula
The symptoms of a vaginal fistula can vary depending on its location and size. Patients may experience an unpleasant odor from the vagina due to the passage of urine or stool through the fistula. Additionally, urine and stool may appear in the vagina, causing irritation and vaginal infections.
Other symptoms of a vaginal fistula may include persistent moisture in the vaginal area, unusual colored or textured discharge, as well as recurrent urinary tract infections. It is important to remember that symptoms can differ among patients, so early detection and diagnosis are crucial steps in determining the presence of a vaginal fistula.
- Unpleasant odor from the vagina: an unpleasant odor may arise due to urine or feces passing through a fistula.
- Vaginal discharge: the appearance of discharge with an unusual color or consistency may be a sign of a vaginal fistula.
- Moisture in the vaginal area: a constant feeling of moisture in this area may indicate the presence of a fistula.
- Possible irritation and infections: the penetration of urine and feces into the vagina may provoke irritation and infections in this area.
- Recurrent urinary tract infections: a vaginal fistula may lead to increased susceptibility to urinary tract infections.
Approach to the treatment of vaginal fistula: specialists’ opinions
Expert opinion in the field of vaginal fistula treatment emphasizes the importance of an individualized approach to patients. Specialists tend to agree that the choice of treatment method should be based on the nature of the fistula, its causes, location, size, and the overall condition of the patient. Research shows that surgical treatment remains the primary method for eliminating vaginal fistulas, but in some cases, conservative therapy may be applied to maintain the condition until surgical intervention.
Modern technologies and medical advancements allow specialists to effectively diagnose and treat vaginal fistulas. Experts recommend seeking medical assistance at the first signs of a fistula, as early intervention can contribute to successful treatment and prevent complications. It is important to consider the opinion of specialists when choosing a treatment method for vaginal fistulas to ensure the best outcomes for the patient.

Methods for diagnosing a vaginal fistula
For the diagnosis of a vaginal fistula, various methods are used, including a vaginal examination, which allows the doctor to assess the areas of the vagina involved in the formation of the fistula and identify possible complications. Performing a colposcopy can help visualize the defect areas on the walls of the vagina and confirm the presence of a fistula. Additionally, ultrasound or computed tomography may be used for more detailed visualization of the affected areas.
Furthermore, specialists may use cystoscopy, rectosigmoidoscopy, or ureteroscopy for a more accurate determination of the position and characteristics of the fistula. This comprehensive approach to diagnosis helps to determine the extent of damage, choose the most effective treatment method, and reduce the risk of complications.
- Vaginal examination: The doctor performs an internal examination of the vagina to assess pathological changes and identify a fistula.
- Colposcopy: This visualization method allows the observation of defective areas on the walls of the vagina and confirms the presence of a fistula.
- Ultrasound examination: Allows for a more detailed investigation of the structure of the pelvic organs and the identification of a fistula within them.
- Computed tomography: Used for additional visualization of the affected areas and to determine the extent of tissue damage.
- Cystoscopy, rectosigmoidoscopy, urethroscopy: Additional examination methods that help determine the location and characteristics of the fistula with maximum accuracy.
Methods for treating vaginal fistula
In some cases, a combined approach is recommended, which includes the use of local procedures and surgical treatment to improve outcomes. The choice of treatment method for vaginal fistulas depends on their size, location, causes of formation, accompanying diseases, and the patient’s condition. An individualized approach to treatment allows for the best outcomes and reduces the risk of recurrence.
- Surgical intervention: Includes defect reconstruction using fresh epithelial tissues or autologous material.
- Local procedures: Include the use of gauze tampons and antiseptics to aid in tissue healing.
- Combined approach: A combination of local procedures and surgical treatment to enhance outcome effectiveness.
- Individualized approach: The choice of treatment method depends on the size, location, and causes of the fistula formation, as well as the patient’s condition.
- Application of modern techniques and technologies: Includes the use of endoscopic methods and innovative surgical approaches to reduce the risk of complications and improve treatment outcomes.
Prevention measures for vaginal fistula
Regular check-ups with a gynecologist allow for the detection of early-stage pathologies and timely treatment, thereby reducing the risk of developing a vaginal fistula. It is also important to avoid untrusted self-treatment methods, and when necessary, consult a qualified medical specialist for the timely detection and treatment of any diseases of the female reproductive system.
- Timely treatment of infections: Preventing and timely treating vaginal infections helps avoid possible complications such as vaginal fistula.
- Regular check-ups with a gynecologist: Conducting routine examinations and tests with a doctor helps detect pathologies at early stages and take measures for their treatment, reducing the risk of developing a vaginal fistula.
- Avoiding traumatic interventions: One should refrain from undergoing traumatic procedures or surgeries in the pelvic area to prevent tissue damage and the development of fistulas.
- Exclusion of self-medication: It is important to avoid using unreliable treatment methods and to consult a qualified medical specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment of women’s reproductive system diseases.
- Observance of hygiene rules: Daily hygiene procedures, the proper choice of hygiene products, as well as the use of natural underwear help reduce the risk of inflammatory processes and fistulas in the vagina.
Interesting aspects of treating a vaginal fistula
Furthermore, research in the field of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering is opening up prospects for the use of biomaterials and cellular technologies in the treatment of vaginal fistulas. These advanced methods may contribute to more effective recovery of damaged tissues and improved treatment outcomes.