Understanding Lymph Node Inflammation: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Methods
- The basics of lymph node inflammation
- Etiology of lymph node inflammation
- The clinical picture of lymph node inflammation
- Treatment of lymph node inflammation: expert opinions.
- Diagnosis of lymph node inflammation
- Methods for treating lymph node inflammation
- Measures to prevent inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Interesting aspects of lymph node inflammation
- FAQ
The basics of lymph node inflammation
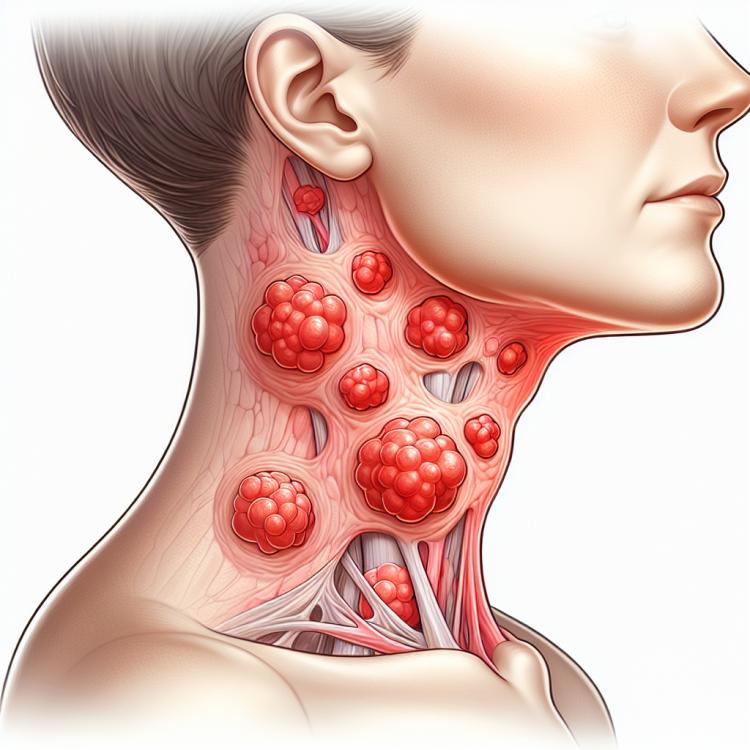
Inflammation of the lymph nodes, or lymphadenitis, manifests as a reaction of the immune system to infection or other inflammatory processes in the body. The lymph nodes play a key role in defending against infections by filtering lymph and destroying microbes. When there are disorders in the lymphatic system or in the case of infection, the lymph nodes may enlarge, become painful, and sensitive.
Manifestations of lymph node inflammation can include pain, swelling, redness, and increased skin temperature in the surrounding area. Diagnosis includes examination by a doctor, laboratory blood tests, ultrasound, as well as a biopsy if necessary. It is important to seek medical help promptly if lymph node inflammation is suspected to determine the cause and provide appropriate treatment.
Etiology of lymph node inflammation
The etiology of lymphadenitis is often related to infectious processes, where various pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, can trigger the activation of the immune system and subsequent inflammation of the lymph nodes. For example, bacterial infections, such as streptococcal or staphylococcal infections, are often accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes in nearby areas.
In addition to infections, other causes of lymph node inflammation include oncological diseases, immune disorders, and reactions to medications. It is important to conduct a thorough examination of the patient to identify the underlying cause of the lymph node inflammation and determine the optimal treatment approach.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can cause inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Oncological diseases: Cancerous tumors can lead to the enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Immune disorders: Autoimmune diseases can cause improper functioning of the immune system, which can lead to inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Reaction to medications: Some medications can cause allergic reactions, leading to inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Vaccination: Shots and vaccination can cause a temporary increase in lymph nodes in response to the body’s immune response.
The clinical picture of lymph node inflammation
The clinical picture of lymph node inflammation includes various symptoms such as enlargement of the lymph nodes, tenderness upon touch, redness of the skin in the area of the lymph nodes, and sometimes fever. Patients often report general malaise, weakness, and a deteriorating state of health.
For an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will conduct a physical examination and may order laboratory tests, including a blood test and ultrasound examination of the lymph nodes. If there are symptoms of lymph node inflammation, it is important to timely consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and the initiation of appropriate treatment.
- Enlargement of lymph nodes: usually, lymph nodes become enlarged and palpable in case of inflammation.
- Tenderness upon touch: pain or discomfort may occur when pressing on inflamed lymph nodes.
- Redness of the skin in the area of lymph nodes: inflammation may be accompanied by a change in skin color around the affected nodes.
- Fever: in some cases, inflammation of the lymph nodes is accompanied by fever and general malaise.
- General condition: patients often report weakness, fatigue, and other general symptoms associated with the inflammatory process in the body.
Treatment of lymph node inflammation: expert opinions.
Experts in the field of medicine recommend an individualized approach to treating lymph node inflammation depending on the underlying cause. For infectious processes, the prescription of antibiotics or antiviral drugs is often required; however, in the case of tumors or other diseases, surgical intervention or radiation therapy may be necessary. Specialists also emphasize the importance of monitoring the overall condition of the patient, recommending regular follow-up and consultations with specialists.
Effective treatment of lymph node inflammation not only aims to relieve symptoms but also to eliminate the underlying disease. Thanks to modern diagnostic and treatment methods, experts provide patients with high-quality and comprehensive medical care, striving for the best outcomes in the fight against this pathology.

Diagnosis of lymph node inflammation
The diagnosis of lymph node inflammation usually begins with a physical examination of the patient, including palpation of the lymph nodes to determine their size, consistency, and tenderness. Additional diagnostic methods may include blood tests to identify inflammatory markers, ultrasound to assess the structure of the lymph nodes, lymph node biopsy to determine the nature of the inflammation, or other educational methods depending on the clinical picture.
It is important to pay due attention to the diagnosis of lymph node inflammation, as accurately determining the cause and nature of the inflammation can dictate the further therapeutic approach and prognosis of the disease for the patient. Only an integrated approach that takes into account clinical data, laboratory studies, and instrumental methods will achieve an accurate diagnosis and allow for effective treatment.
- Physical examination: Includes palpation of lymph nodes, assessment of size, consistency, and tenderness.
- Blood test: Conducted to investigate the level of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein and the number of leukocytes.
- Ultrasound examination: Allows evaluation of the structure and nature of changes in lymph nodes during inflammatory processes.
- Lymph node biopsy: A procedure in which a sample of lymph node tissue is taken for more detailed analysis and determination of the cause of inflammation.
- Imaging methods: Include computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for more detailed visualization of changes in the lymphatic system.
Methods for treating lymph node inflammation
Other treatment methods for lymph node inflammation may include physiotherapy, the use of compresses, recommendations for rest and reduction of physical activity, and in some cases, surgical intervention to remove lymph nodes or formations if they have become the cause of the disease. Patients should consult a medical specialist to determine the optimal approach to treating lymph node inflammation, taking into account individual characteristics and the clinical picture of the disease.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: Prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain syndrome in the affected lymph nodes.
- Antibiotics/antiviral drugs: Used in cases of infectious inflammation to eliminate the causative agents of the infection.
- Physiotherapy: May be prescribed to improve blood circulation and reduce swelling in the area of the inflamed lymph nodes.
- Surgical intervention: Necessary in some cases, especially with formations or nodular formations, to remove affected tissues.
- Complications and alleviating measures: Used to reduce swelling and decrease pain sensations in the area of the inflamed lymph nodes.
Measures to prevent inflammation of the lymph nodes
Additionally, vaccination against infectious diseases known for their ability to cause lymph node inflammation may play an important role in prevention. It is advisable to consult a medical professional to develop individualized prevention programs for lymph node inflammation based on the patient’s unique characteristics and potential disease risks.
- Maintaining hygiene, including regular hand washing, is a key factor in preventing the transmission of infections and the occurrence of lymph node inflammation.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical exercise, a diverse and nutritious diet, and healthy sleep, contributes to improving immunity and reducing the risk of inflammatory conditions.
- Vaccination against infectious diseases, whose pathogens can lead to lymph node inflammation, is an important measure for the prevention of these conditions.
- Avoiding contact with infectious sources and using personal protective equipment when necessary also helps reduce the risk of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes.
- Regular check-ups and consultations with a doctor help to identify problems at an early stage and timely initiate preventive measures aimed at preventing lymph node inflammation.
Interesting aspects of lymph node inflammation
Moreover, lymph node inflammation can be a sign of serious diseases, such as oncological conditions or systemic diseases of the immune system. Monitoring the condition of the lymph nodes and timely consulting a doctor when they become enlarged or painful is an important aspect of health care and the prevention of complications.