Liver cirrhosis: causes, symptoms, and treatment
- Definition of Liver Cirrhosis
- Risk factors for the development of liver cirrhosis
- Immediate signs of liver cirrhosis
- The opinion of specialists on the treatment of liver cirrhosis
- Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
- Approaches to the treatment of liver cirrhosis
- Prevention of liver cirrhosis
- Amazing facts about liver cirrhosis
- FAQ
Definition of Liver Cirrhosis
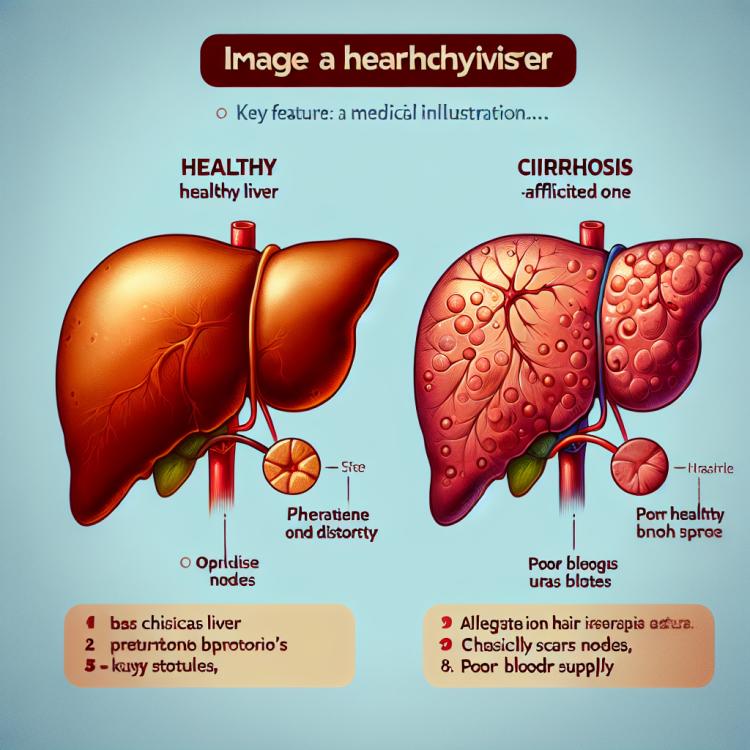
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic and progressive liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy tissue substrate with connective tissue. This pathological process leads to the disruption of the normal architecture of the liver, loss of its function, and possible development of complications such as ascites, portal hypertension, and liver failure.
Liver cirrhosis can occur due to various causes, including alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, and autoimmune diseases. Although this process is irreversible, early detection and timely treatment can slow the progression of the disease and improve the prognosis for the patient.
Risk factors for the development of liver cirrhosis
The development of liver cirrhosis is associated with various risk factors, including long-term alcohol abuse, viral infections (such as hepatitis B and C), as well as chronic liver diseases like fatty liver disease. Other contributing factors to the development of cirrhosis include autoimmune liver diseases, genetic disorders, inadequate nutrition, and obesity.
Understanding these risk factors plays an important role in the prevention and management of liver cirrhosis. Effective vaccines against viral infections of hepatitis B and C, interventions to stop alcohol abuse, and regular monitoring of liver condition can reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis and improve prognosis for patients.
- Alcohol abuse: Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages can lead to chronic liver damage, contributing to the development of cirrhosis.
- Viral infections: Hepatitis B and C infections are among the main causes of liver cirrhosis.
- Fatty liver disease: Accumulation of fat in the liver, caused by an unhealthy lifestyle or other factors, can lead to the further development of cirrhosis.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some immune system disorders can lead to damage to liver cells and the development of cirrhosis.
- Genetic factors: Hereditary factors can also influence susceptibility to the development of liver cirrhosis.
Immediate signs of liver cirrhosis
Symptoms of liver cirrhosis can manifest in various ways, including fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, and weight loss. Patients often experience discomfort and pain in the upper abdomen, as well as swelling in the legs and abdomen due to fluid retention in the body.
In the later stages of liver cirrhosis, serious complications may arise, such as a yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), the development of blood vessels on the skin (spider veins), bleeding from the esophageal veins, ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity), and mental changes. At the first signs of liver cirrhosis, it is important to consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Fatigue and weakness: Patients with liver cirrhosis may experience persistent fatigue and weakness due to liver dysfunction and lack of energy.
- Loss of appetite: A lack of interest in food and loss of appetite are often observed in patients with liver cirrhosis due to digestive system dysfunction.
- Nausea: Frequent or constant feelings of nausea may also be a symptom of liver cirrhosis, related to metabolic disturbances.
- Weight loss: Patients with liver cirrhosis may lose weight due to loss of appetite, reduced food intake, and metabolic dysfunction.
- Abdominal discomfort: Pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen may be signs of liver cirrhosis due to liver enlargement and the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
The opinion of specialists on the treatment of liver cirrhosis
Experts in the fields of gastroenterology and hepatology emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to treating liver cirrhosis, which may include medication therapy, diet, exercise, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Early seeking of medical assistance and strict adherence to the physician’s prescriptions play a key role in managing the condition of a patient with cirrhosis.
Experts also highlight the necessity of regular monitoring of liver condition for the timely detection of complications and adjustment of treatment. An individualized approach to each patient, taking into account the specifics of their condition and lifestyle, as well as the constant updating of treatment methods based on new scientific discoveries and clinical research, are important aspects for the successful management of liver cirrhosis.

Diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
The diagnosis of liver cirrhosis involves various methods and studies to assess the condition of the liver and identify areas of fibrosis and scarring. This may include biochemical blood tests, such as measuring liver enzyme levels and bilirubin, as well as tests that evaluate the functional state of the liver. Other diagnostic methods include ultrasound, CT, and MRI, which can help determine the size of the liver, the presence of tissue damage, and other pathological changes.
Additional procedures, such as laparoscopy and liver biopsy, may be prescribed to confirm the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis and determine the extent of organ damage. Accurate diagnosis is a key element of effective management and treatment of liver cirrhosis, so it is important to timely conduct all necessary studies to assess the condition of the liver and choose the optimal treatment strategy.
- Biochemical blood tests: measuring liver enzyme levels, bilirubin, and other indicators to assess the functional state of the liver.
- Ultrasound examination: a visualization method that helps determine the size of the liver, the structure of tissues, and identify possible changes.
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): more detailed diagnostic methods that allow detecting liver lesions and assessing their nature.
- Laparoscopy: a surgical procedure that involves inspecting internal organs using an optical instrument – a laparoscope.
- Liver biopsy: a procedure in which a small piece of liver tissue is extracted for further detailed analysis and confirmation of the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis.
Approaches to the treatment of liver cirrhosis
Additional measures may include lifestyle changes such as stopping alcohol consumption, healthy eating, moderate physical activity, and following medical advice. In some cases, a liver transplant may be required. Early detection of liver cirrhosis and timely initiation of effective treatment are crucial for improving prognosis and preventing complications.
- Treatment of the underlying disease: addressing or controlling the primary cause of liver cirrhosis to prevent further deterioration of the organ’s condition.
- S symptomatic treatment: prescribing medications to improve the quality of life for the patient and alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, and fluid retention.
- Dietary control: recommendations for healthy eating and diet aimed at reducing the burden on the liver and improving its functions.
- Regular monitoring and observation: conducting regular examinations and tests to monitor liver condition, assess treatment effectiveness, and timely identify complications.
- liver transplantation: in cases of severe cirrhosis and ineffectiveness of other treatment methods, liver transplantation may be required as a last resort.
Prevention of liver cirrhosis
Preventing infections from hepatitis B and C viruses also plays a key role in the prevention of liver cirrhosis. Vaccination against hepatitis B and caution when handling infected materials will help protect the body from viral liver damage, which reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis. Regularly following prevention recommendations and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can lower the likelihood of liver diseases, including cirrhosis.
- Reducing or completely stopping alcohol consumption to prevent alcoholic liver cirrhosis.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and physical activity, to support liver functions.
- Regular medical check-ups and monitoring of chronic diseases that may affect liver condition.
- Vaccination against hepatitis B and caution when in contact with infected materials to prevent viral liver infections.
- Avoiding self-medication and the use of narcotic substances, as this can damage the liver and contribute to the development of cirrhosis.
Amazing facts about liver cirrhosis
Another surprising fact about cirrhosis of the liver is that the liver has the ability to self-repair in some injuries; however, this process is weakened in cirrhosis due to the large amount of scar tissue. Therefore, it is important to promptly identify and treat liver diseases to prevent the progression of cirrhosis and related complications.