Endocervicitis: features of diagnosis and treatment methods
Understanding Endocervicitis: Key Points
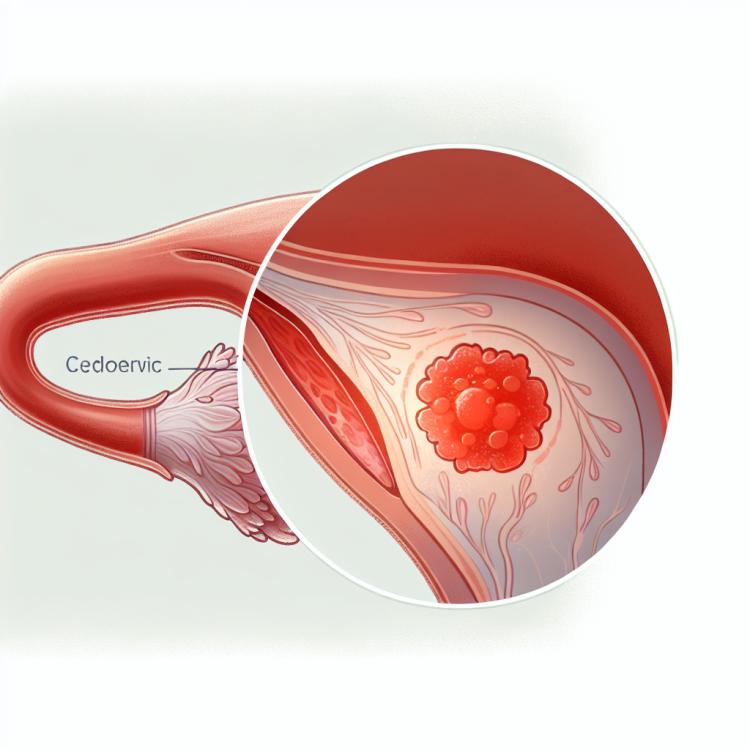
Endocervicitis is an inflammatory process affecting the endocervical canal of the cervix, usually caused by infection. The main symptoms are vaginal discharge, pain, and dysfunctional bleeding. For diagnosis, it is important to conduct a gynecological examination, including a cytological examination of the cervix and bacteriological analysis of the discharge. Treatment may include the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and probiotics, if necessary accompanied by physiotherapy and recommendations to improve hygiene practices.
Pathogenesis of Endocervicitis
Endocervicitis develops due to an inflammatory reaction to an infection, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis. The infection spreads through sexual contact or ascending from the vagina. The mechanism of inflammation development in the endocervix includes the activation of immunity, the release of proteases and cytokines, leading to histological changes and symptoms of inflammation.
- Infection: Endocervicitis is often caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, such as chlamydia, gonococci, or candida.
- Inflammatory response: The development of inflammation occurs in response to infection and involves the activation of immunity and the release of cytokines.
- Histological changes: Inflammation causes tissue changes in the endocervix, such as thickening of the mucosa and an increase in the number of immune cells.
- Cell damage: Infection can damage the cells of the endocervix, increasing their susceptibility to inflammation and further infections.
- Immune variations: Different individual immune responses may affect the course and severity of endocervicitis in different patients.
Clinical picture of Endocervicitis
The clinical picture of endocervicitis usually includes symptoms of inflammation of the cervix, such as vaginal discharge, painful sensations in the lower abdomen, and irregular menstruation. Patients may also experience pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse. The diagnosis is based on the patient’s complaints, gynecological examination, laboratory, and instrumental research methods, such as cervical cytology and biopsy.
- Vaginal discharge: patients may experience increased amounts of discharge, which may be yellowish or greenish.
- Abdominal pain: discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen is possible, especially during palpation.
- Menstrual irregularities: endocervicitis can lead to changes in the menstrual cycle, including abnormal bleeding or more painful periods.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse: during sexual activity, women may experience discomfort or even pain in the cervical area.
- Sensitivity during gynecological examination: during the examination, the gynecologist may note increased sensitivity or tenderness of the cervix in the patient.
Expert opinion on the treatment of Endocervicitis
Experts’ opinions on the treatment of endocervicitis highlight the importance of an individualized approach to each patient. Treatment may include the use of antibiotics to eliminate the infection, anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation, and measures to support and strengthen immunity. However, the choice of treatment method depends on the cause of endocervicitis, the clinical features of the patient, and the opinion of the specialist.
Modern medicine also pays significant attention to preventing recurrences of endocervicitis. Experts recommend regular monitoring of the condition of the cervix, undergoing preventive examinations with a gynecologist, and following all of the specialist’s recommendations. In addition, an important aspect is lifestyle and preventive measures that can help avoid the onset of the disease or its recurrences.

Diagnosis of Endocervicitis
Diagnosis of endocervicitis typically includes a gynecological examination to assess the condition of the cervix and vaginal mucosa, taking swabs for laboratory analysis, such as cytology and microbiological research, as well as conducting colposcopy for a more detailed study of the cervix area. Additional diagnostic methods may include ultrasound of the pelvic organs and biopsy if there is a suspicion of a tumor or the need to rule out other pathologies. A comprehensive approach to diagnosis allows for accurate determination of the presence and degree of inflammation, identification of pathogens, and making an informed decision regarding treatment methods.
- Gynecological examination: the doctor performs an examination of the cervix and vagina to identify signs of inflammation.
- Cytological study: taking smears for cytology helps to assess the cellular composition, identify atypias, and detect infection.
- Bacteriological study: allows for the identification of the causative agent of the infection and the selection of appropriate antibiotic therapy.
- Colposcopy: this examination allows for a more detailed study of the tissues of the cervix using a special instrument.
- Ultrasound examination: conducted to assess the condition of the pelvic organs and rule out other pathologies.
Treatment of Endocervicitis
- Use of antibiotics: in the case of a bacterial infection, antibiotics that are active against the infectious agent are usually prescribed.
- Use of antiviral medications: in the case of viral etiology of endocervicitis, treatment with antiviral medications may be required.
- Progestogens to correct hormonal background: in the case of hormonal disorders, the use of progestogens may be appropriate to normalize hormonal balance.
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs: to reduce inflammation and symptoms, anti-inflammatory medications are sometimes prescribed.
- Maintaining hygiene and a healthy lifestyle: it is important to maintain genital hygiene and lead an active lifestyle to improve the effectiveness of treatment and prevent recurrences.
Prevention of Endocervicitis
- Hygiene of the genital organs: regular washing of the genital organs using a gentle gel or soap helps prevent the development of infections.
- Use of condoms: the use of condoms during sexual intercourse helps reduce the risk of transmitting infections, including the agents of endocervicitis.
- Regular visits to the gynecologist: preventive visits to a specialist allow for early detection of pathologies and effective treatment.
- Maintaining a proper diet and a healthy lifestyle: strengthening the immune system with a balanced diet and physical activity helps prevent the development of inflammatory processes.
- Avoiding stress: stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections, including endocervicitis.