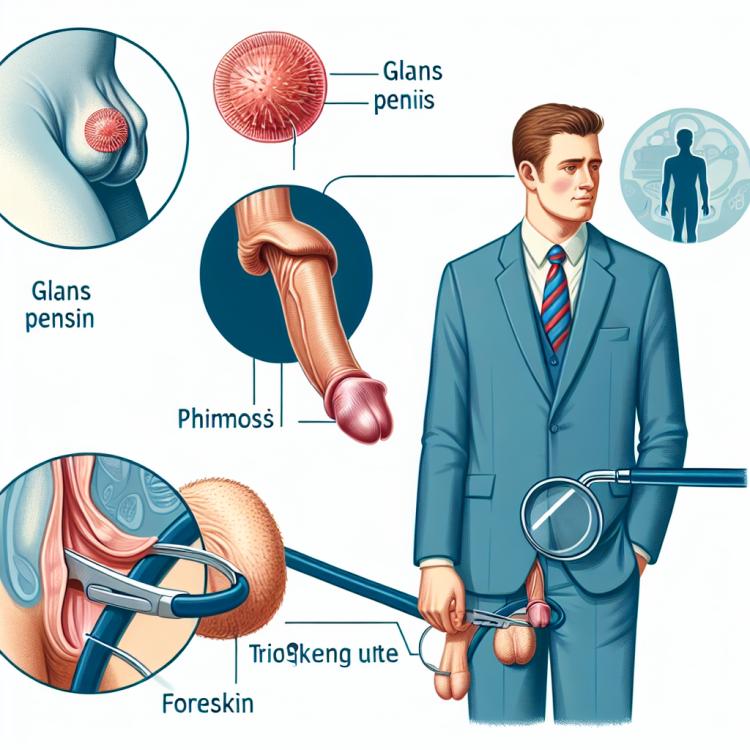
Phimosis: causes, symptoms, and treatment methods
Information about phimosis: causes, symptoms, and treatment
Phimosis is a condition in which the foreskin of the penis cannot be fully retracted due to a narrow opening. Causes of phimosis can include congenital abnormalities, inflammatory processes, or injuries. Symptoms may include pain and discomfort during urination, inability to retract the foreskin, or its inflammation. Treatment of phimosis may involve conservative methods such as topical treatment or surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying causes of phimosis.
Etiology of phimosis
Phimosis, a condition in which the foreskin cannot normally retract over the glans of the penis, can have many causes. One of the main causes of phimosis is a congenital condition where the foreskin is tightly narrow and cannot move freely. Injuries, inflammatory processes, and other medical conditions can also contribute to the development of phimosis. A thorough assessment of the underlying cause of phimosis plays an important role in determining the optimal treatment for this condition.
- Congenital anomalies: a narrow or inelastic foreskin from birth.
- Injuries: damage that can cause scarring and narrowing of the foreskin.
- Inflammatory processes: infections or inflammation can lead to swelling and narrowing of the foreskin.
- Inadequate care measures: improper care of the penis can contribute to the development of phimosis.
- Developmental anomalies: rare genetic or chromosomal disorders may predispose to the development of phimosis.
Clinical picture of phimosis
The clinical picture of phimosis can be diverse and depends on the degree of narrowing of the foreskin. Patients with phimosis may experience difficulties in retracting or exposing the glans penis, which can lead to pain, discomfort, and sometimes bleeding when trying to pull back the foreskin. In adolescents and men, phimosis may also manifest as difficulties in urination, increased sensitivity of the glans penis, and a greater propensity to urinate.
In some patients, phimosis can increase the risk of urinary tract infections and other complications. The diagnosis of phimosis includes physical examination, medical history, and sometimes laboratory tests. Early detection of phimosis symptoms and timely consultation with a doctor for assessment of symptoms and the selection of optimal treatment play an important role in managing this condition.
- Pain and discomfort: patients with phimosis may experience pain and discomfort when retracting the foreskin, especially when exposing the glans penis.
- Difficulty with urination: in some patients, phimosis can lead to difficulties with urination due to the restriction of free movement of the foreskin.
- Increased sensitivity of the glans penis: in phimosis, the glans penis may be more sensitive due to improper protection and stimulation.
- Bleeding: attempts to retract the foreskin in patients with phimosis may lead to bleeding due to tissue damage.
- Risk of urinary tract infections: people with phimosis are at an increased risk of developing urinary tract infections due to difficulties with hygiene and possible urinary retention.
Expert opinions on the treatment of phimosis
Experts’ opinions on the treatment of phimosis highlight several approaches depending on the severity of the case. The primary goal of treating phimosis is to improve the mobility of the foreskin to ensure proper hygiene and prevent complications. In cases where conservative methods are ineffective, surgical intervention may be necessary, such as a circumcision procedure, to prevent further constriction and ensure normal anatomy of the penis.
Experts also emphasize the importance of patient education and awareness regarding personal hygiene practices to prevent recurrences and the development of complications. Timely medical consultation, collaborative treatment planning between the doctor and the patient, as well as attention to the individual characteristics of each case, are key aspects of the successful treatment of phimosis according to experts.

Diagnosis of phimosis
Diagnosis of phimosis typically includes a physical examination of the penis in a state of rest and under medication anesthesia to determine the degree of narrowing of the foreskin and its mobility. The doctor may also perform a visual assessment of the glans penis, checking for inflammation or complications. If necessary, additional diagnostic methods may be applied to evaluate the condition of the urogenital system and exclude other pathologies, such as ultrasound examination or urethroscopy.
An important aspect of diagnosing phimosis is gathering a complete medical history of the patient, including information about possible injuries, inflammations, previously conducted treatments, and other diseases of the reproductive system. A more thorough study of the symptoms and history contributes to a more accurate diagnosis, as well as determining the optimal treatment strategy for this condition.
- Physical examination: examination of the penis in a resting state and under anesthesia allows the doctor to assess the degree of foreskin narrowing and its mobility.
- Visual assessment: the doctor conducts an examination of the glans penis, checks for inflammatory processes, evaluates color, skin condition, and the presence of complications.
- Additional diagnostic methods: if necessary, additional methods such as ultrasound examination of the penis may be used to assess structural abnormalities.
- Medical history analysis: collection of detailed medical history from the patient, including information on possible injuries, inflammation, previous treatments, and other genital system diseases.
- Thorough analysis of symptoms: a more detailed study of the clinical manifestations and symptoms of phimosis, such as difficulty retracting the foreskin, can help in determining the patient’s condition and choosing the optimal treatment strategy.
Treatment of phimosis
- Conservative approaches: The initial stage of treating phimosis may involve the use of specialized ointments or urethral dilators to stretch the foreskin under the supervision of a doctor.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where phimosis is accompanied by complications or conservative methods do not bring results, a surgical procedure such as circumcision or posthetomy may be required.
- Individual approach: Treatment for phimosis should be specifically tailored for each patient, considering their individual characteristics, the degree of narrowing of the foreskin, and the presence of additional diseases.
- Prevention of complications: The goal of treating phimosis also includes preventing possible complications such as urinary tract infections and other issues related to the narrowing of the foreskin.
- Discussion with a doctor: Patients with phimosis should consult a medical specialist to determine the optimal treatment plan and subsequent examinations for effective management of this condition.
Prevention of phimosis
- Maintaining proper hygiene of the genital organs.
- Regular care of the foreskin, especially in children.
- Retracting the foreskin as early as childhood to prevent phimosis in the future.
- Timely consultation with a doctor when signs of phimosis or other problems with the genital organs arise.
- Discussing phimosis prevention issues with a pediatrician or urologist for recommendations and next steps.