
Тубоотит (евстахиит): причины, симптомы и методы лечения
- Определение и основные характеристики тубоотита (евстахиита)
- Etiology of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Symptoms of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Expert Opinions on the Treatment of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Diagnostic Approach for Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Management of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Prevention of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Fascinating Facts About Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
- Вопросы по теме
Определение и основные характеристики тубоотита (евстахиита)
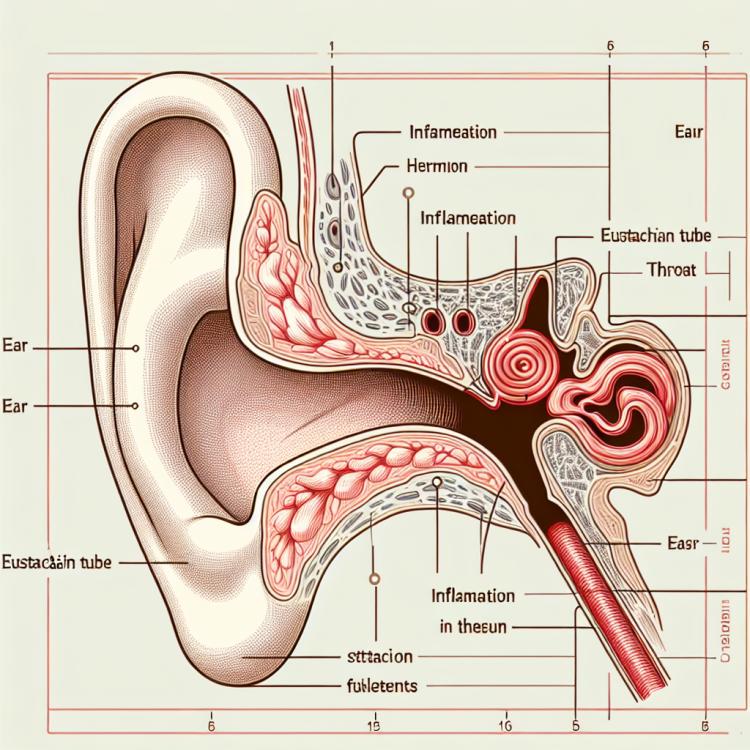
Тубоотит, также известный как евстахиит, представляет собой воспалительное заболевание евстахиевой трубы, которая соединяет среднее ухо с горлом. Ключевыми характеристиками тубоотита являются зуд в ухе, боль и заложенность ушей, а также нарушение слуха. При обострении заболевания может наблюдаться отсутствие отделяемого из уха и повышение температуры тела.
Механизм развития тубоотита обычно связан с инфекцией, аллергическими реакциями или нарушениями функции евстахиевой трубы. Лечение этого заболевания может включать применение противовоспалительных препаратов, местных средств для носа и горла, физиотерапевтические процедуры и, в некоторых случаях, антибактериальные препараты.
Etiology of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Etiology of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) includes a variety of factors. Acute tubootitis is commonly caused by viral upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold, which lead to inflammation and blockage of the Eustachian tube. Chronic or recurrent cases may be attributed to allergies, nasal polyps, chronic sinusitis, or anatomical variations in the Eustachian tube. Dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can also be a result of sudden changes in barometric pressure, such as during air travel or scuba diving, leading to barotrauma.
Other factors contributing to tubootitis can include smoking, exposure to environmental irritants, immune system disorders, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In children, enlarged adenoids are a common cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Understanding the underlying causes of tubootitis is essential for appropriate diagnosis and management of this condition, as addressing the root cause can lead to effective treatment strategies and symptom relief.
- Вирусные инфекции: Одной из распространенных причин тубоотита являются вирусные респираторные инфекции, которые приводят к воспалению и блокировке Евстахиевой трубы.
- Аллергии: Аллергические реакции могут способствовать развитию длительного или повторяющегося тубоотита.
- Анатомические особенности: Вариации в строении Евстахиевой трубы могут способствовать ее дисфункции.
- Курение и воздействие окружающей среды: Курение и контакт с раздражителями окружающей среды могут ухудшить функцию Евстахиевой трубы.
- Системные заболевания: Некоторые системные заболевания, такие как рефлюксное эзофагит (GERD) или нарушения иммунной системы, могут способствовать развитию тубоотита.
Symptoms of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Symptoms of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) can vary depending on the severity and duration of the condition. Patients may experience ear pain, pressure, or fullness due to the impaired ventilation of the middle ear. Hearing loss or muffled hearing can also occur as a result of the Eustachian tube dysfunction, affecting the transmission of sound waves to the inner ear.
Additionally, patients with tubootitis may present with tinnitus, which is characterized by ringing or buzzing sounds in the ear. Some individuals may report dizziness or vertigo, especially if the dysfunction is associated with inner ear disturbances. The presence of recurrent ear infections or fluid accumulation behind the eardrum may further contribute to the symptomatology of tubootitis. Understanding these signs and symptoms is crucial for the accurate diagnosis and management of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Ear Pain: Patients with tubootitis may experience sharp or dull pain in the affected ear, often described as aching or throbbing.
- Pressure Sensation: A common symptom of Eustachian tube dysfunction is the sensation of pressure or fullness in the ear, similar to the feeling of having a blocked or plugged ear.
- Hearing Difficulties: Impaired ventilation of the middle ear can lead to hearing loss, muffled sounds, or a sense of decreased hearing acuity.
- Tinnitus: Ringing, buzzing, or other abnormal sounds in the ear, known as tinnitus, may be present in individuals with tubootitis.
- Dizziness or Vertigo: Some patients may experience a spinning sensation (vertigo) or lightheadedness as a symptom of Eustachian tube dysfunction, particularly if inner ear disturbances are involved.
Expert Opinions on the Treatment of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Expert opinions on the treatment of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) emphasize a multi-faceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific condition. Specialists often recommend initial conservative methods such as nasal decongestants, antihistamines, and nasal corticosteroid sprays to alleviate nasal congestion and reduce Eustachian tube inflammation. Additionally, experts highlight the importance of addressing underlying factors like allergic rhinitis or sinus infections to prevent recurrent Eustachian tube dysfunction.
In cases where conservative measures are ineffective, experts may consider more advanced interventions such as tympanostomy tube placement to facilitate middle ear ventilation or surgical procedures to correct anatomical abnormalities. Collaboration among otolaryngologists, allergists, and other healthcare providers ensures comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plans for individuals with Tubootitis, aligning with the current evidence-based practices to optimize patient outcomes.

Diagnostic Approach for Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
The diagnostic approach for Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction) involves a thorough clinical evaluation to assess the patient’s medical history and presenting symptoms. Otoscopy may reveal signs of inflammation or fluid behind the eardrum, indicating Eustachian tube dysfunction. Audiometric tests, such as tympanometry and pure tone audiometry, can help assess middle ear function and detect any associated hearing loss.
In some cases, imaging studies like computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized to evaluate the anatomy of the Eustachian tube and surrounding structures. Tympanocentesis, a procedure where fluid is extracted from the middle ear for analysis, may be performed to confirm the presence of infection. The diagnostic process aims to accurately identify the underlying cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction, guiding the selection of appropriate treatment strategies for the individual patient.
- Clinical Evaluation: Assessment of medical history and symptoms to identify potential causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Otoscopy: Examination of the ear canal and eardrum for signs of inflammation, fluid, or structural abnormalities indicative of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Audiometric Tests: Utilization of tympanometry and pure tone audiometry to evaluate middle ear function and detect any associated hearing loss.
- Imaging Studies: Consideration of computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize the Eustachian tube and related anatomical structures.
- Tympanocentesis: In some cases, extraction of middle ear fluid for analysis may be performed to confirm the presence of infection as a potential cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Почему b-healthy clinic?
Management of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
In cases where Eustachian tube dysfunction persists or is recurrent, further medical interventions like tympanostomy tubes insertion may be considered to facilitate middle ear ventilation and drainage. Antibiotics may be prescribed in cases of acute otitis media or secondary ear infections. Surgical options, such as Eustachian tube dilation procedures, may be indicated for refractory cases. The selection of treatment modalities is tailored to the individual patient based on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and response to initial therapies.
- Conservative Measures: Techniques like swallowing, yawning, or the Valsalva maneuver can promote Eustachian tube opening.
- Nasal Decongestants: Use of nasal decongestants or corticosteroid nasal sprays can help reduce nasal congestion and inflammation, improving Eustachian tube function.
- Tympanostomy Tubes: Insertion of tympanostomy tubes may be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent Eustachian tube dysfunction to aid middle ear ventilation and drainage.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to manage acute otitis media or secondary ear infections associated with Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Surgical Interventions: For refractory cases, surgical options such as Eustachian tube dilation procedures may be recommended to address persistent Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Prevention of Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Practicing proper techniques to equalize ear pressure during air travel, scuba diving, or rapid changes in altitude can help prevent barotrauma and subsequent Eustachian tube dysfunction. Additionally, timely treatment of upper respiratory infections and prompt management of conditions such as allergies, sinusitis, or adenoid hypertrophy can aid in preventing complications that may lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Education about risk factors and early recognition of symptoms can empower individuals to take proactive measures in preventing Tubootitis.
- Nasal Hygiene: Maintain good nasal hygiene by avoiding allergens and irritants, regular nasal saline irrigation, and treating nasal conditions promptly to prevent congestion and inflammation affecting Eustachian tube function.
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking and minimize exposure to environmental pollutants to reduce the risk of Eustachian tube dysfunction and associated complications.
- Ear Pressure Equalization Techniques: Learn and practice proper techniques to equalize ear pressure during activities like air travel, scuba diving, or rapid altitude changes to prevent barotrauma and Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Prompt Treatment of Infections: Early recognition and timely management of upper respiratory infections can help prevent complications that may lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Education and Awareness: Educate individuals about risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures for Tubootitis to empower them to take proactive steps in maintaining ear health and preventing Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Fascinating Facts About Tubootitis (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction)
Moreover, certain risk factors, such as smoking, allergies, and anatomical variations in the Eustachian tube, can predispose individuals to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with Tubootitis is essential for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies. Research continues to explore innovative approaches to managing and preventing Eustachian tube dysfunction, highlighting the importance of ongoing advancements in otolaryngology and ear health.
